Network Topologies
Network Topologies
Useful in planning a new network
- Physical layout of a building or campus
Assists in understanding signal flow
- Troubleshooting problems
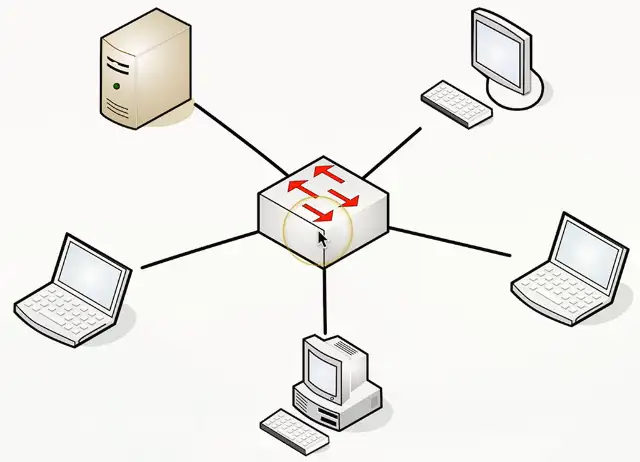
Star/Hub and Spoke
Used in most large and small networks
All devices are connected to a central device
Switched Ethernet networks
- The switch is in the middle
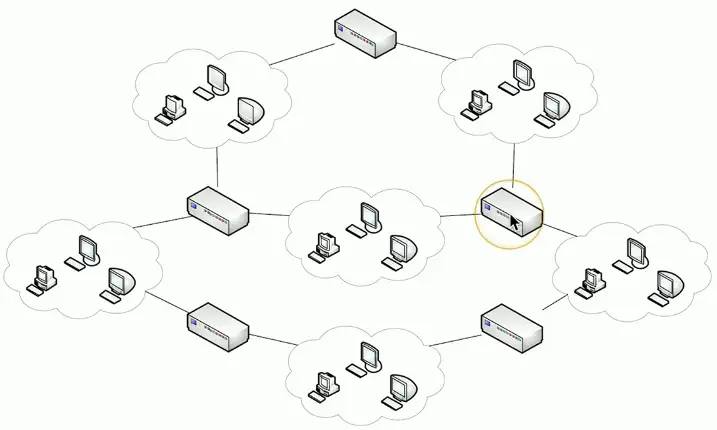
Mesh
Multiple links to the same place
- Fully connected
- Partially connected
Redundancy, fault-tolerance, load balancing
Used in wide area networks (WANs)
- Fully meshed and partially meshed
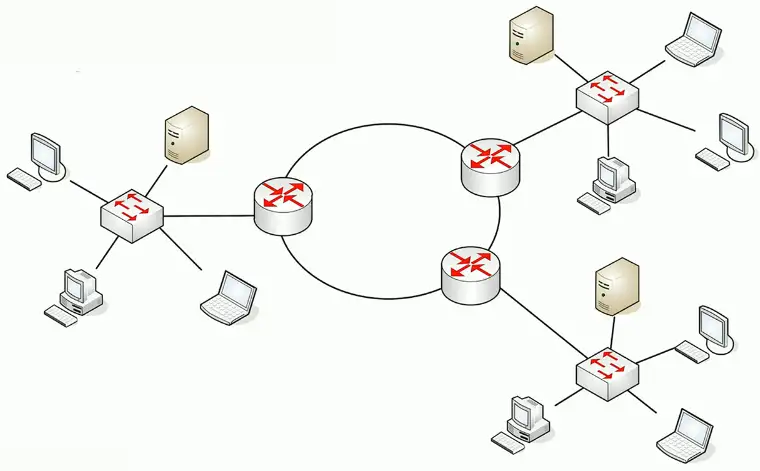
Hybrid
A combination of one or more physical topologies
- Most networks are a hybrid
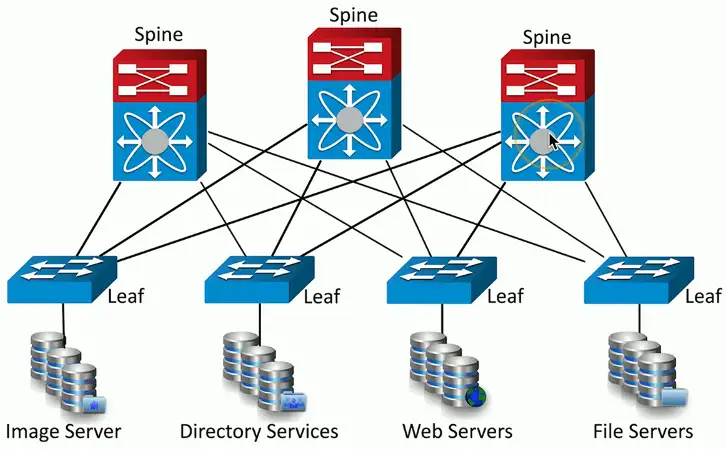
Spine and Leaf Architecture
Each leaf switch connects to each spine switch
- Each spine switch connects to each leaf switch
Leaf switches don’t connect to each other
- Same for spine switches
Top-of-rack switching
- Each leaf is on the “top” of a physical network rack
- May include a group of physical racks
Advantages
- Simple cabling
- Redundant
- Fast
Disadvantages
- Additional switches may be costly
Point-to-point
One-to-one connection
Older WAN links
- Point to point T-1
Connections between buildings
Network Architectures
Three-tier architecture
Core
- The “center” of the network
- Web servers, databases, applications
- Many people need access to this
Distribution
- A midpoint between the core and the users
- Communication between access switches
- Manage the path to the end users
Access
- Where the users connect
- End stations, printers
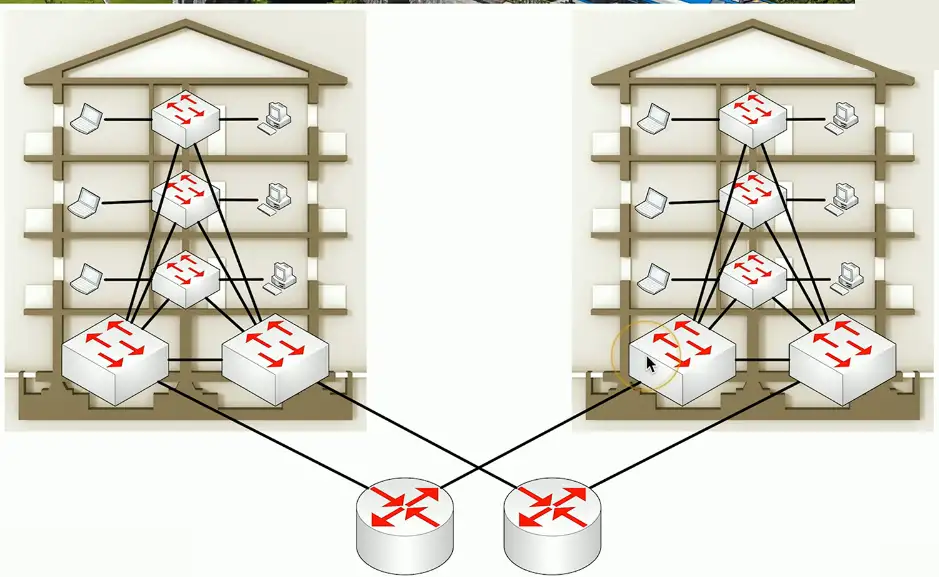
Collapsed Core
A two-tier model
- Simplify the three-tier architecture
- A good fit for smaller organizations
Combine Core and Distribution layers
- Collapse together
Differences over three-tier
- Simpler to design and support
- Less expensive to implement
- Not as resilient
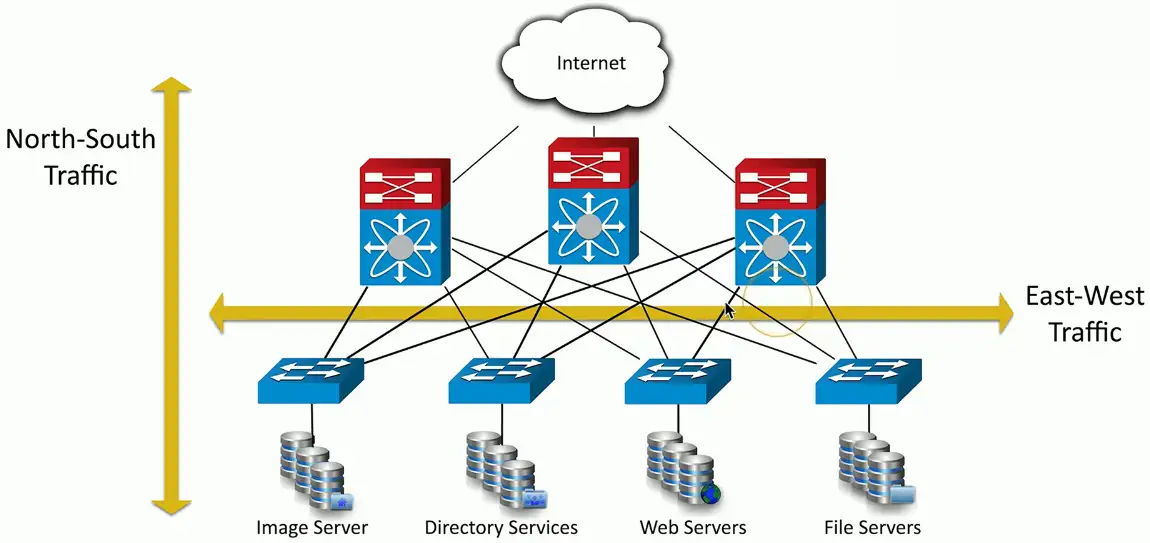
Traffic Flows
Traffic flows within a data center
- Important to know where traffic starts and ends
East-west
- Traffic between devices in the same data center
- Relatively fast response times
North-south traffic
- Ingress/egress to an outside device
- A different security posture than east-west traffic