Python Data Structures
Tuples
-
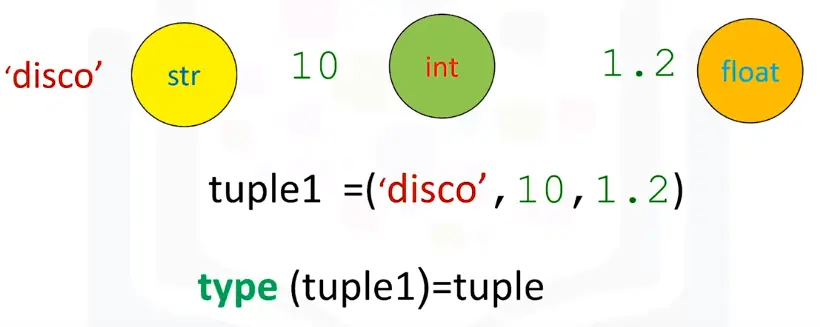
Tuples are an ordered sequence
-
Here is a Tuple “Ratings”
-
Tuples are written as comma-separated elements within parentheses
-
Tuples concatenation is possible
-
Tuple slicing is also possible
-
Tuples are immutable
-
If one want to manipulate tuples, they have to create a new tuple with the desired values
-
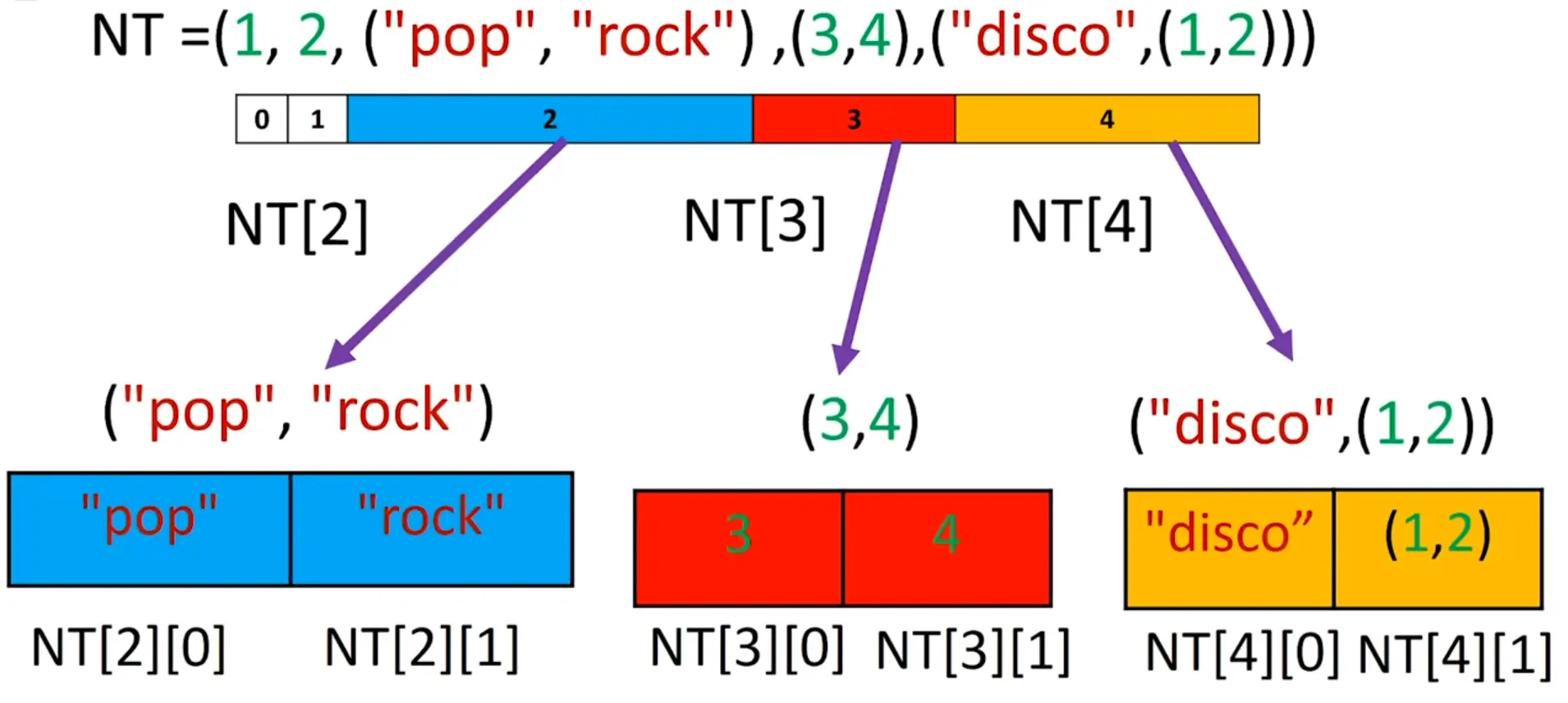
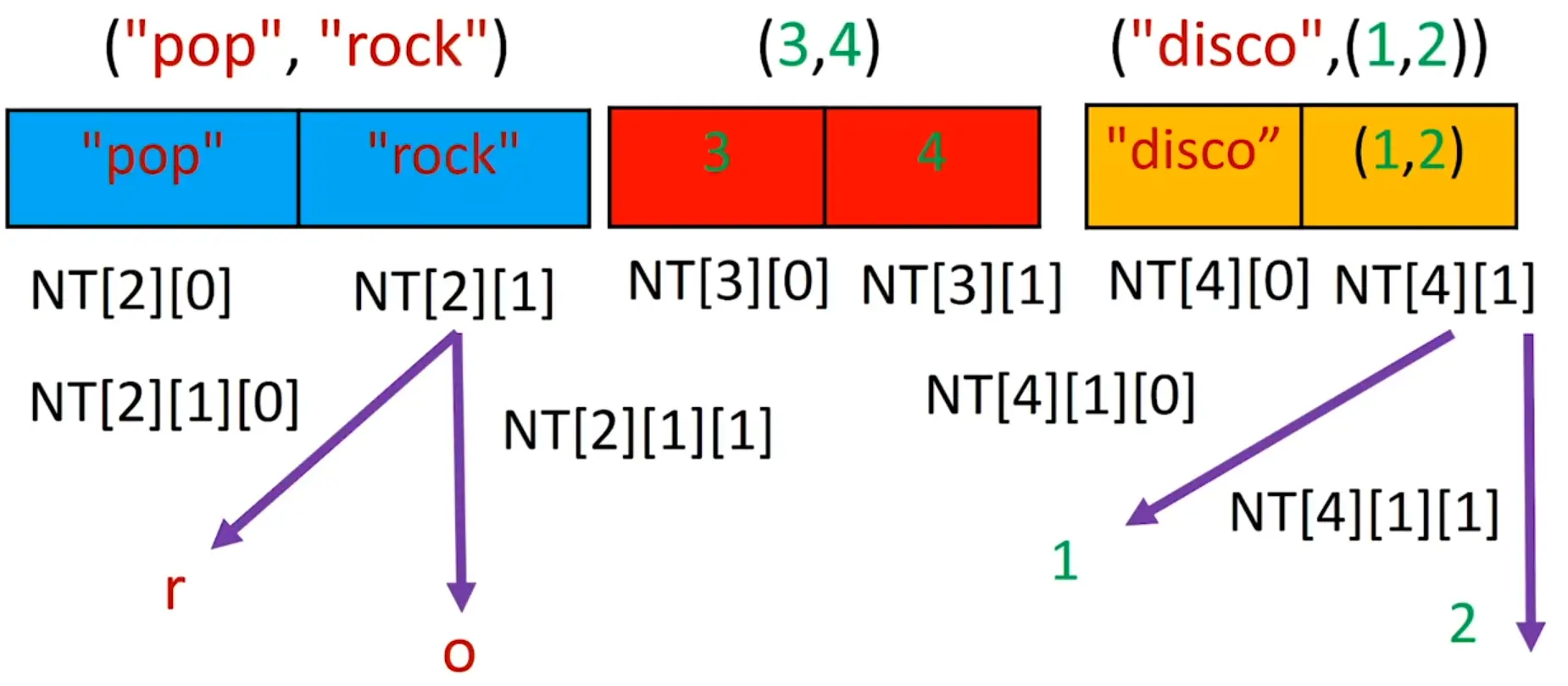
Tuples nesting (tuple containing another tuple) is also possible
Lists
-
Lists are also ordered in sequence
-
Here is a List “L”
-
A List is represented with square brackets
-
List is mutable
-
List can nest other lists and tuples
-
We can combine lists
-
List can be extended with
extend()method -
append()adds only one element to the List, if we appendL.append([1,2,3,4]), the List “L” will be: -
The method
split()can convert the string into the List -
The
split()can be used with a delimiter we would like to split on as an argument -
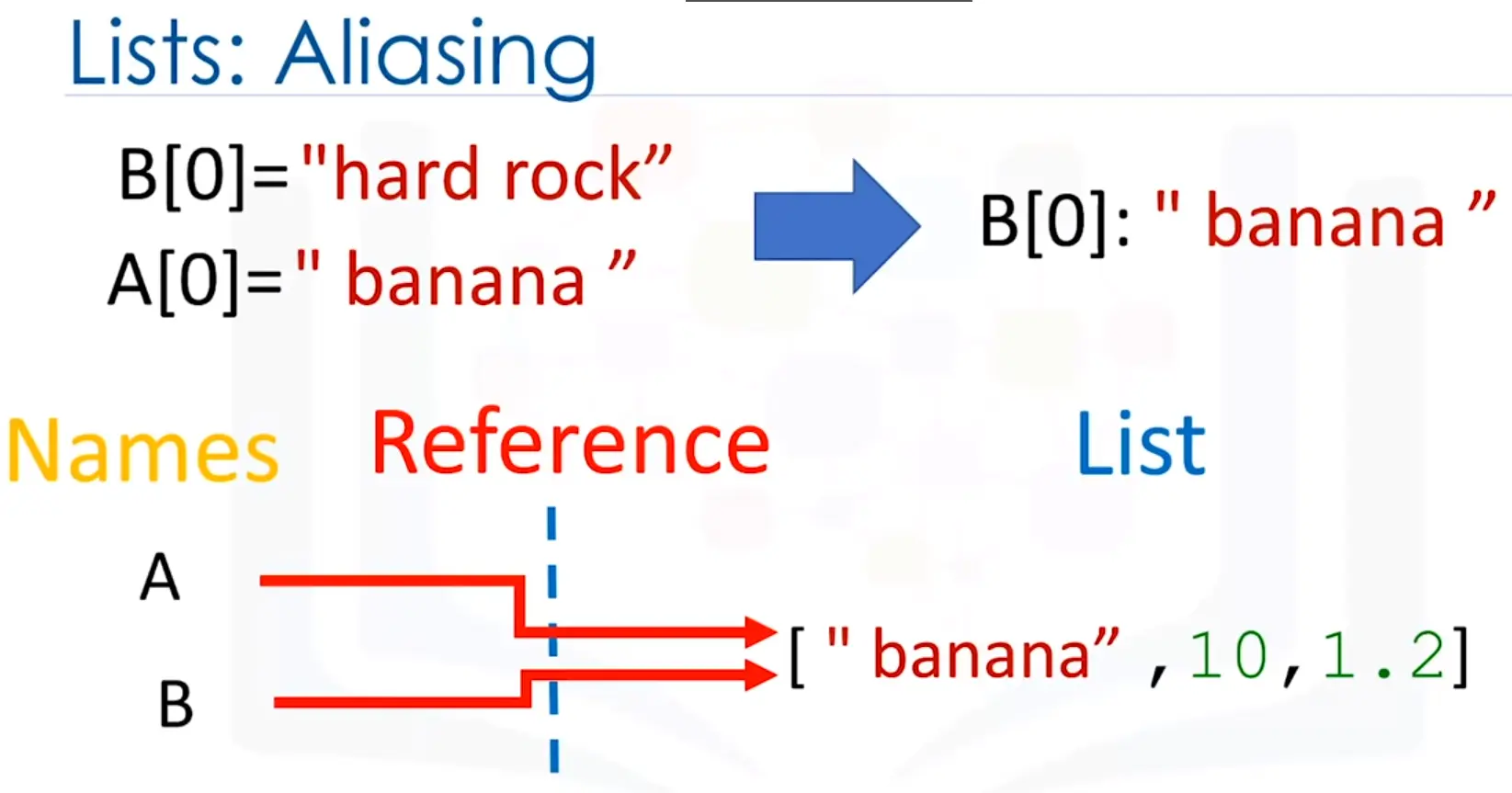
Multiple names referring to the same object is known as aliasing
- We can clone the list, where both lists will be of their independent copies
- So changing List “A”, will not change List “B”
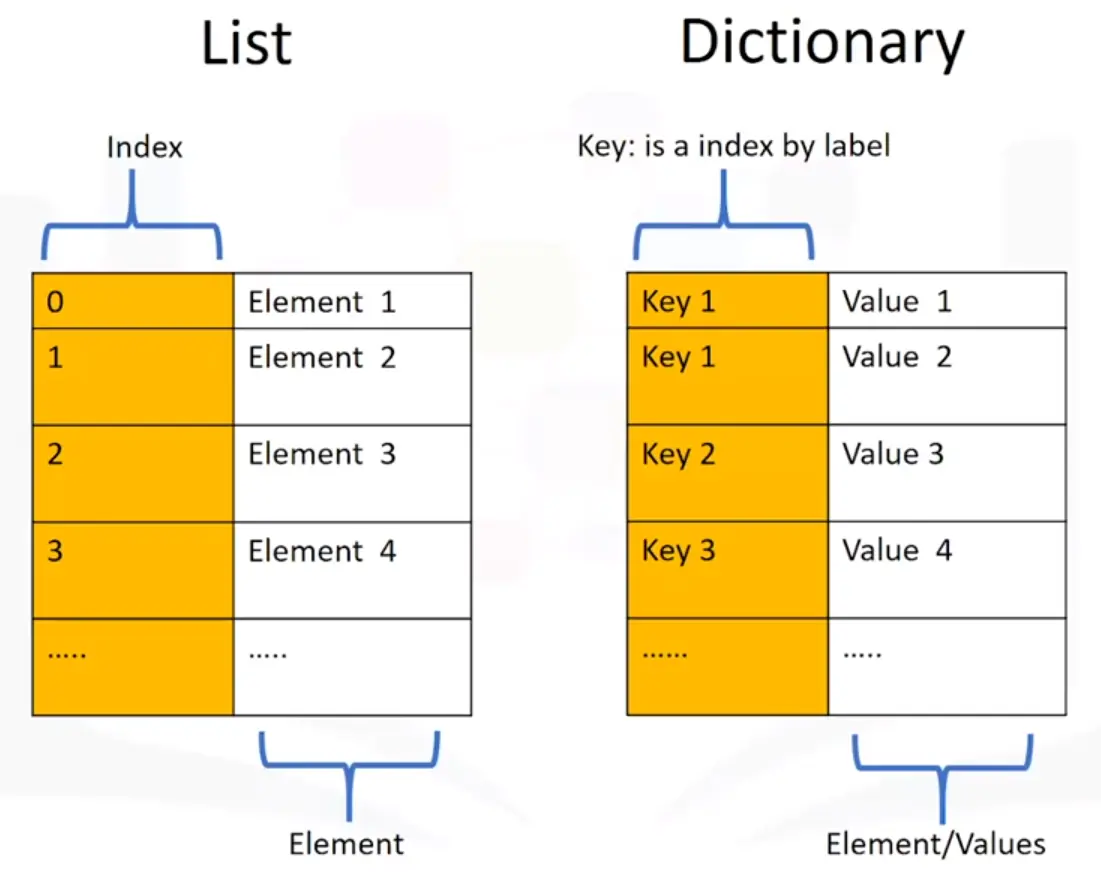
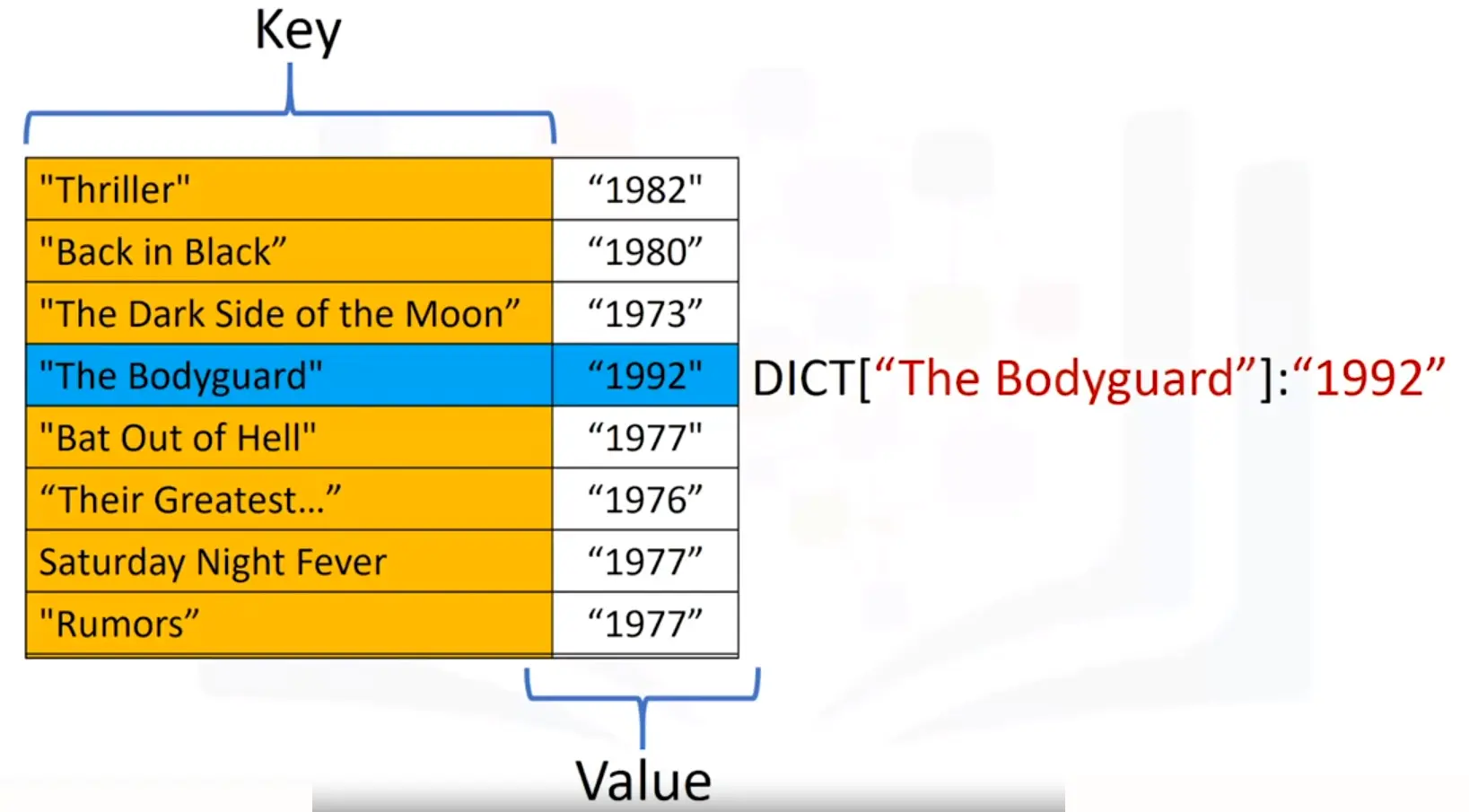
Dictionaries
- Dictionaries are denoted with curly Brackets {}
- The keys have to be immutable and unique
- The values can be immutable, mutable and duplicates
- Each key and value pair is separated by a comma
Sets
- Sets are a type of collection
- This means that like lists and tuples you can input different python types
- Unlike lists and tuples they are unordered
- This means sets don’t record element position
- Sets only have unique elements
- This means there is only one of a particular element in a set
Sets: Creating a Set
-
You can convert a list into set
-
To add elements to the set,
set.add('foo') -
To remove an element,
set.remove(‘foo’) -
To check if an element is present in the set:
Sets: Mathematical Expression
- To find the intersection of the sets elements present in the both sets),
set1 & set2orset1.intersection(set2)
-
Union of the sets, contain elements of both the sets combined,
set1.union(set2) -
To find the difference of sets:
- To find is a set is a subset/superset (have all the elements of other set), `set1.issubset/issuperset(set2)