Security Data Sources
Log Data
Security Log Files
Detailed security-related information
- Blocked and allowed traffic flows
- Exploit attempts
- Blocked URL categories
- DNS sinkhole traffic
Critical security information
- Documentation of every traffic flow
- Summary of attack info
- Correlate with other logs
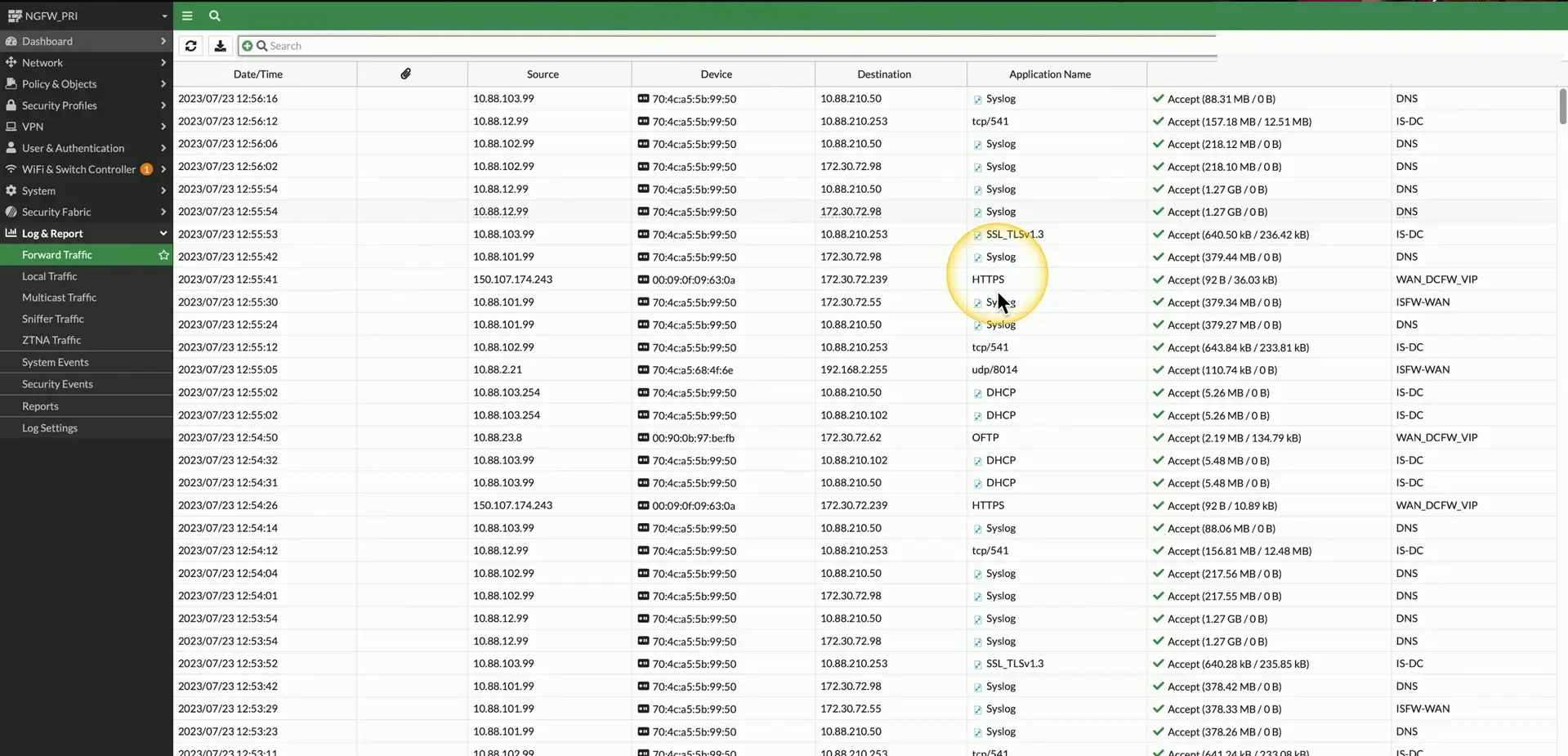
Firewall logs
Traffic flows through the firewall
- Source/destination IP, port numbers, dispositions
Next Generation Firewalls (NGFW)
- Logs the application used, URL filtering categories, anomalies and suspicious data
Application Logs
Specific to the application
- Information varies widely
Windows
- Event Viewer/Application Log
Linux/macOS
- /var/log
Parse the log details on the SIEM
- Filter out unneeded info
Endpoint Logs
Attackers often gain access to endpoints
- Phones, laptops, tablets, desktops, servers, etc.
There’s a lot of data on the endpoint
- Logon events, policy changes, system events, processes, account management, directory services, etc.
Everything rolls up to the SIEM
- Security Information and Event Manager
Use with correlation of security events
- Combine IPS events with endpoint status
OS-specific Security Logs
OS security events
- Monitoring apps
- Brute-force, files changes
- Authentication details
Find problems before they happen
- Brute force attacks
- Disabled services
May require filtering
- Don’t forward everything
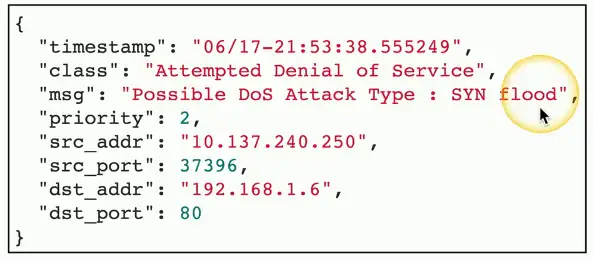
IPS/IDS Logs
IPS/IDS
- Usually integrated into an NGFW
Logs contain information about predefined vulnerabilities
- Known OS vulnerabilities, generic security events
Common data points
- Timestamps
- Type or class of attack
- Source and destination IP
- Source and destination port
Network Logs
Switches, routers, access points, VPN concentrators
- And other infrastructure devices
Network changes
- Routing updates
- Authentication issues
- Network security issues
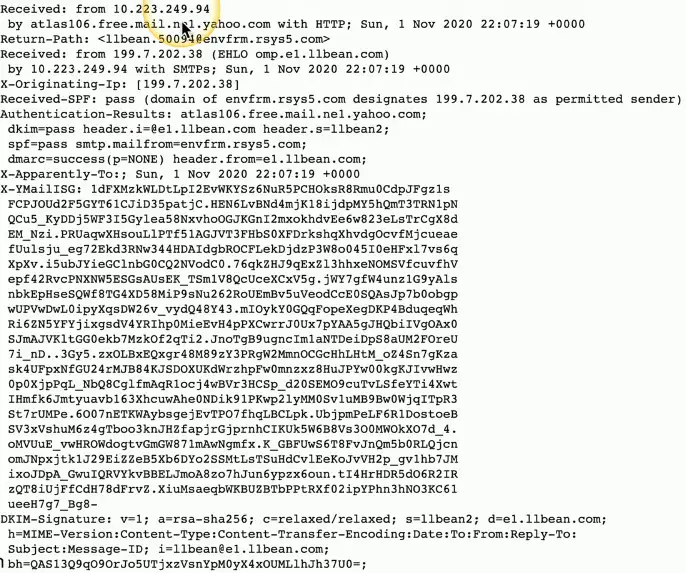
Metadata
Metadata
- Data that describes other data sources
- Header details, sending servers, destination address
Mobile
- Type of phone, GPS location
Web
- OS, browser type, IP address
Files
- Name, address, phone number, title
Vulnerability Scan
Lack of security controls
- No firewall
- No anti-virus
- No anti-malware
Misconfigurations
- Open shares
- Guest access
Real vulnerabilities
- Especially newer ones
- Occasionally the old ones
Automated Reports
Most SIEMs include a report generator
- Automate common security reports
May be easy or complex to create
- The SIEM may have its own report generator
- Third-party report generators may be able to access the database
Requires human intervention
- Someone has to read the reports
These can be involved to create
- Huge data storage and extensive processing time
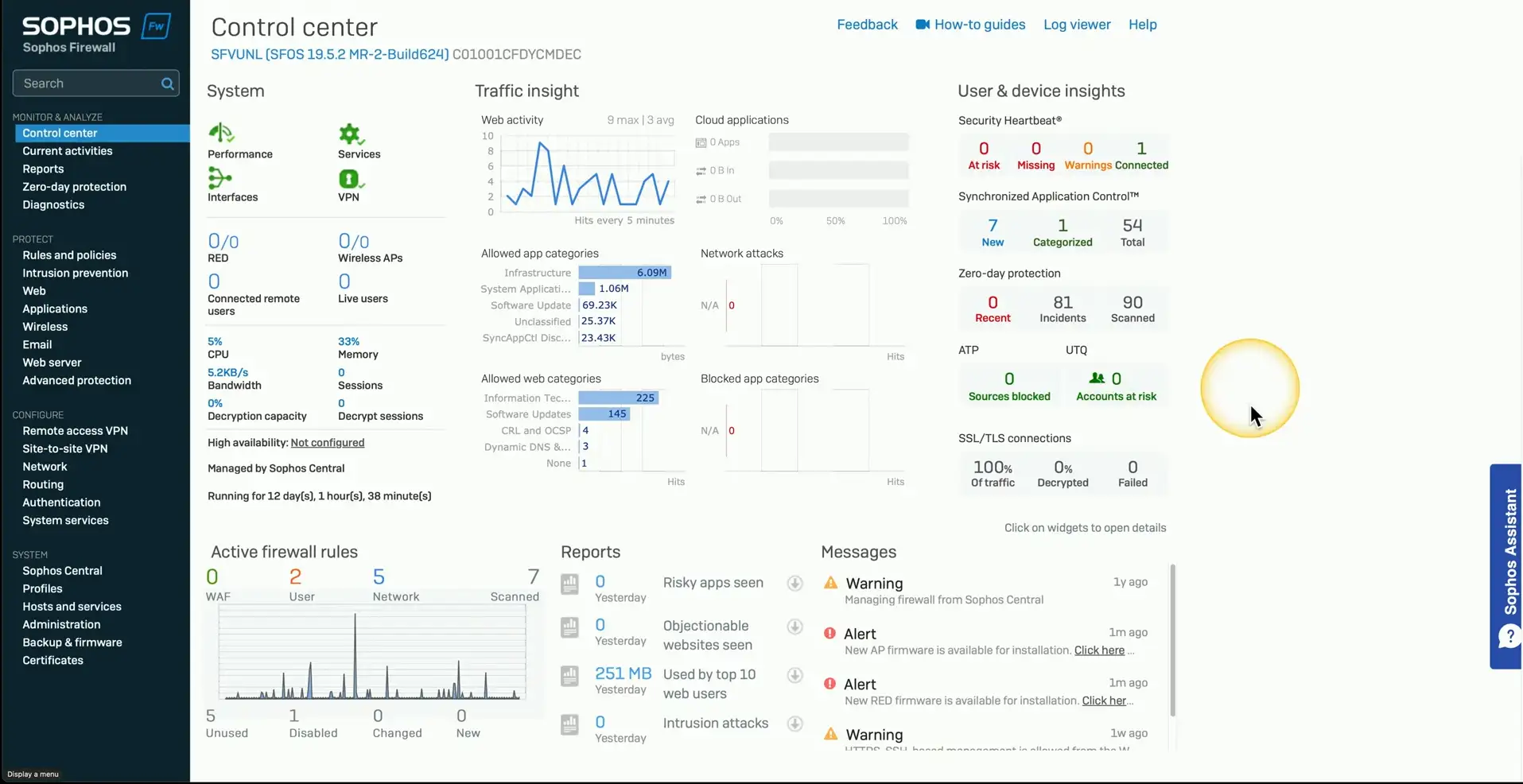
Dashboards
Real-time status information
- Get summaries on a single screen
Add or remove information
- Most SIEMs and reporting systems allow for customization
Shows the most important data
- Not designed for long-term analysis
Packet Captures
Solve complex application issues
- Get into the details
Gathers packets on the network
- Or in the air
- Sometimes built into the device
View detailed traffic information
- Identify unknown traffic
- Verify packet filtering and security controls
- View a plain-language description of the application data