Common Threat Vectors
A method used by the attacker
- Gain access or infect to the target
- Also called “Attack Vectors”
A lot of work goes into finding vulnerabilities in these vectors
- Some are more vulnerable than others
IT security professional spend their career watching these vectors
- Protect existing vectors
- Find new vectors
Message-based Vectors
One the biggest (and most successful) threat vectors
- Everyone has at least one of these messaging systems
- Malicious links in an email
- Link to malicious site
SMS (Short Message Service
- Attacks in a text message
Phishing Attacks
- People want to click links
- Links in an email, links send via text or IM
Deliver the malware to the user
- Attach it to the email
- Scan all attachments, never launch untrusted links
Social engineering attacks
- Invoice scams
- Cryptocurrency scams
Image-based Vectors
Easy to identify a text-based threat
- It’s more difficult to identify the threat in an image
Some image formats can be a threat
- The SVG (Scalable Vector Graphic) format
- Image is described in XML (Extensible Markup Language)
Significant security concerns
- HTML injection
- JavaScript attack code
Browsers must provide input validation
- Avoid running malicious code
File-based Vectors
More than just executables
- Malicious code can hide in many places
Adobe PDF
- A file format containing other objects
ZIP/RAR files (or any compression type)
- Contains many files
Microsoft Office
- Documents with macros
- Add-in files
Voice Call Vectors
Vishing
- Phishing over the phone
Spam over IP
- Large-scale phone calls
War dialing
- It still happens
Call tampering
- Disrupting voice calls
Removable Device Vectors
Get around the firewalls
- The USB interface
Malicious software on USB flash drives
- Infect air gapped networks
- Industrial systems, high-security services
USB devices can act as keyboards
- Hacker on a chip
Data exfiltration
- Terabytes of data walk out the door
- Zero bandwidth used
Vulnerable Software Vectors
Client-based
- Infected executable
- Known (or unknown) vulnerabilities
- May require constant updates
Agentless
- No installed executable
- Compromised software on the server would affect all users
- Client runs a new instance each time
Unsupported Systems Vectors
Patching is an important prevention tool
- Ongoing security fixes
Unsupported systems aren’t patched
- There may not even be an option
Outdated OSes
- Eventually, even the manufacturer won’t help
A single system could be an entry
- Keep your inventory and records current
Unsecure Network Vectors
The network connect everything
- Ease of access for the attackers
- View all (non-encrypted) data
Wireless
- Outdated security protocols (WEP, WPA, WPA2)
- Open or rogue wireless networks
Wired
- Unsecure interfaces — No 802.1X
Bluetooth
- Reconnaissance
- Implementation vulnerabilities
Open Service Ports
Most network-based services connect over a TCP or UDP port
- An “open” port
Every open port is an opportunity for the attacker
- Application vulnerability or misconfiguration
Every application has their own open port
- More services expand the attack surface
Firewall rules
- Must allow traffic to an open port
Default Credentials
Most devices have default usernames and passwords
- Change yours!
The right credentials provide full control
- Administrator access
Very easy to find the defaults for your access point or router
Supply Chain Vectors
Tamper with the underlying infrastructure
- Or manufacturing process
Managed service providers (MSPs)
- Access many customer networks from one location
Gain access to a network using a vendor
- 2013 Target credit card breach
Suppliers
- Counterfeit networking equipment
- Install backdoors, substandard performance and availability
- 2020 — Fake Cisco Catalyst Switches
Phishing
Social engineering with a touch of spoofing
- Often delivered by email, text, etc.
- Very remarkable when well done
Don’t be fooled
- Check the URL
Usually there’s something not quite right
- Spelling, fonts graphics
Business Email Compromise
We trust email sources
- The attackers take advantage of this trust
Spoofed email addresses
- Not really a legitimate email address
- professor@professormessor.com
Financial fraud
- Send emails with updated bank information
- Modify wire transfer details
The recipient clicks the links
- The attachments have malware
Tricks and Misdirection
How are they so successful?
- Digital slight of hands
- It fools the best of us
Typo squatting
- A type of URL hijacking — https://professormessor.com
Pretexting
- Lying to get information
- Attacker is a character in a situation they create
- Hi, we are calling from Visa regarding an automated payment to your utility service
Phishing with different bait
Vishing (voice phishing) is done over the phone or voicemail
- Call ID spoofing is common
- Fake security checks or bank updates
Smishing (SMS phishing) is done by text message
- Spoofing is a problem here as well
- Forwards links or asks for personal information
Variations on a theme
- The fake check scam, phone verification code scam, Boss/CEO scam, advance-fee scam
- Some great summaries on https://reddit.com/r/Scams
Impersonation
Attackers pretend to be someone they are not
- Halloween for the fraudsters
User some of those details from reconnaissance
- You can trust me, I’m with your help desk
Attack the victim as someone higher in rank
- Office of the Vice President for Scamming
Throw tons of technical details around
- Catastrophic feedback due to the depolarization of the differential magnetometer
Be a buddy
- How about those Cubs
Eliciting Information
Extracting information from the victim
- The victim doesn’t even realize this is happening
- Hacking the human
Often seen with vishing
- Can be easier to get this information over the phone
These are well-documented psychological techniques
- They cannot just ask, “So, what’s your password?”
Identify Fraud
Your identity can be used by others
- Keep your personal information safe!
Credit card fraud
- Open an account in your name, or use your credit card information
Bank Fraud
- Attacker gains access to your account or opens a new account
Loan fraud
- Your information is used for a loan or lease
Government benefits fraud
- Attacker obtains benefits on your behalf
Protect against impersonation
Never volunteer information
- My password is 12345
Don’t disclose personal details
- The bad guys are tricky
Always verify before revealing info
- Call back, verify through 3rd parties
Verification should be encouraged
- Especially if your organization owns valuable information
Watering Hole Attack
Watering hole is a computer attack strategy in which an attacker guesses or observes which websites an organization’s users frequent, and then uses one or more of the websites to distribute malware.
What if your network was really secure?
- You didn’t even plug in that USB key from the parking lot
The attackers can’t get in
- Not responding to phishing emails
- Not opening any email attachments
Have the mountain come to you
- Go where the mountain hangs out
- the watering hole
- This requires a bit of research
Executing the Watering Hole Attack
Determine which websites the victim group uses
- Educated guess — Local coffee or sandwich shop
- Industry-related sites
Infect one of these third-party sites
- Site vulnerability
- Email attachments
Infect all visitors
- But you are just looking for specific victims
- Now you’re in!
Because that’s where the money is
January 2017
Polish Financial Supervision Authority, National Banking and Stock Commission of Mexico, State-owned bank in Uruguay
- The watering hole was sufficiently poisoned
Visiting the site would download malicious JavaScript files
- But only to IP addresses matching banks and other financial institutions
Did the attack work?
- We still don’t know
Watching the Watering Hole
Defense-in-depth
- Layered defense
- It’s never one thing
Firewall and IPS
- Stop the network traffic before things get bad
Antivirus/Anti-malware signature updates
- The Polish Financial Supervision Authority attack code was recognized and stopped by generic signatures in Symantec’s antivirus software
Other Social Engineering Attacks
Misinformation/disinformation
Disseminate factually incorrect information
- Create confusion and division
Influence campaigns
- Sway public opinion on political and social issues
Nation-state actors
- Divide, distract, and persuade
Advertising is an option
- Buy a voice for your opinion
Enabled through Social media
- Creating, sharing, liking, amplifying
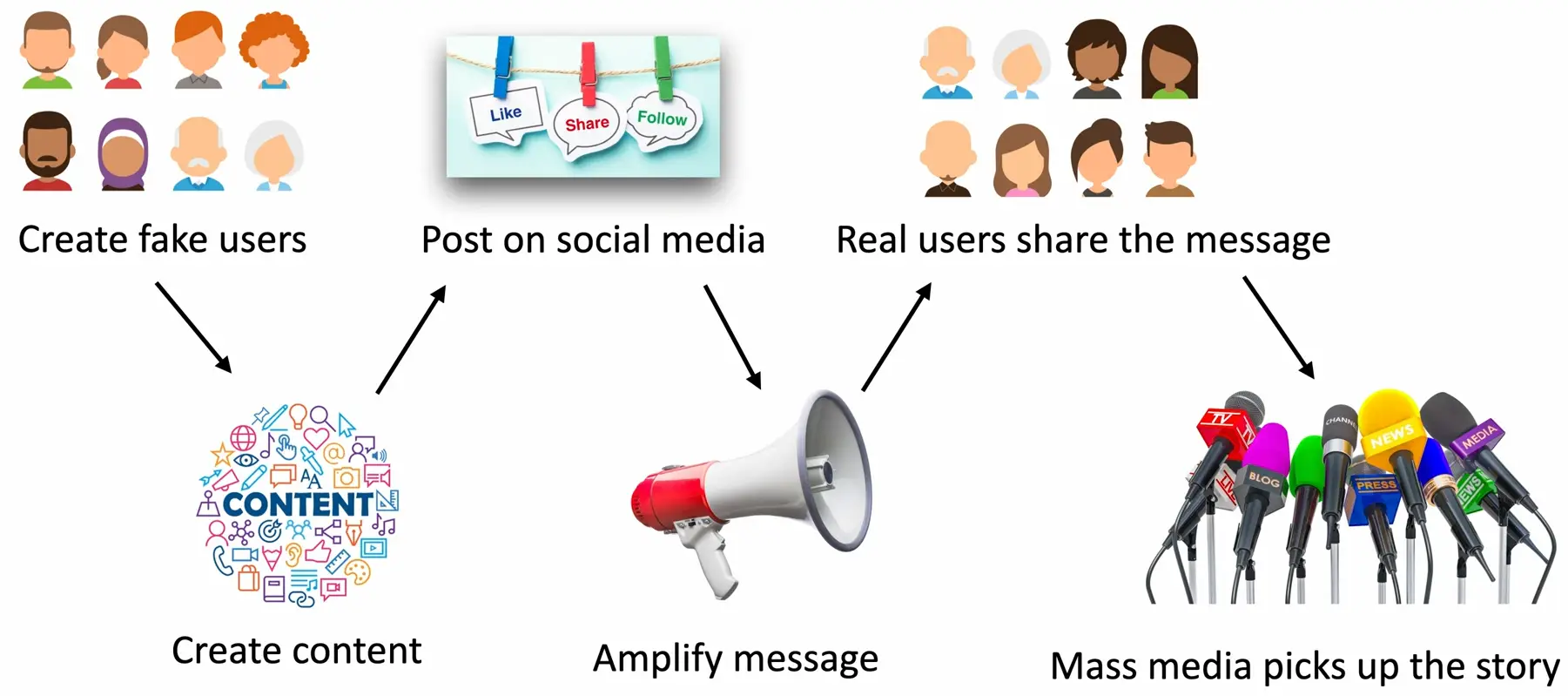
The misinformation Process
Brand Impersonation
Pretend to be a well-known brand
- Coca-cola, McDonald’s, Apple, etc.
Create tens of thousands of impersonated sites
- Get into the Google index, click an ad, get a WhatsApp message
Visitors are presented with a pop-up
- You won! Special offer! Download the video!
Malware infection is almost guaranteed
- Display ads, site tracking, data exfiltration