Risk Management
Risk Management
Risk Identification
The only certainty is uncertainty
- Risk management helps to understand potential risks
- Identify weaknesses before they become an issue
An important part of any organization
- Growth brings risk
- It’s useful to get ahead of any potential problems
Risk management
- Manage potential risk
- Qualify internal and external threats
- Risk analysis helps plan for contingencies
Performing a risk Assessment
Not all risk requires constant evaluation
- Or it might be required to always assess the amount of risk
One-time
- The assessment may be part of a one-time project
- Company acquisition, new equipment installation, unique new security threats, etc.
Continuous assessments
- May be part of an existing process
- Change control requires a risk assessment as part of the change
Ad HOC Assessment
An organization may not have a formal risk assessment process
- Perform an assessment when the situation requires
CEO is back from a conference
- Wants to know if the organization is protected from a new attack type
A committee is created, and the risk assessment proceeds
- Once the assessment is complete, the committee is disbanded
- There may not be a need to investigate this specific risk again
Recurring Assessment
Recurring assessments
- The evaluation occurs on standard intervals
An internal assessment
- Performed every three months at the beginning of the quarter
A mandated risk assessment
- Required by certain organizations
- Some legal requirements will mandate an assessment
- PCI DSS requires annual risk assessments
Risk Analysis
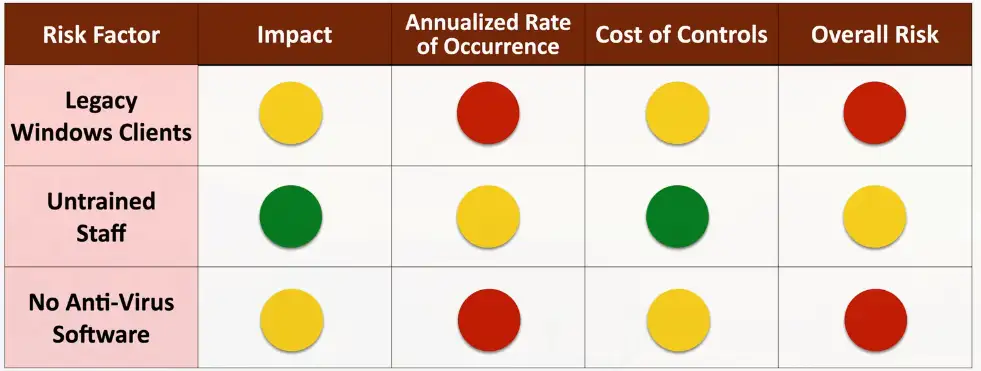
Qualitative Risk Assessment
Identify significant risk factors
- Ask opinions about the significance
- Display visually with traffic light grid or similar method
ARO (Annualized Rate of Occurrence)
- How likely is that a hurricane will hit? In Montana? In Florida?
Asset value (AV)
- The value of asset to the organization
- Includes the cost of the asset, the effect of company sales, potential regulatory fines, etc.
Exposure factor (EF)
- The percentage of the value lost due to an incident
- Losing a quarter of the value is
.25 - Losing the entire asset is
1.0
SLE (Single Loss Expectancy)
- What is the monetary loss if a single event occurs?
Asset value (AV) x Exposure factor (EF)Laptop stolen = $1000 (AV) x 1.0 (EF) = $1000 (SLE)
ALE (Annualized Loss Expectancy)
Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO) x SLESeven laptops stolen a year (ARO) x $1000 (SLE) = $7000
The business impact can be more than monetary
Quantitative vs. qualitative
Impact
Life
- The most important consideration
Property
- The risk to buildings and assets
Safety
- Some environments are too dangerous to work
Finance
- The resulting financial cost
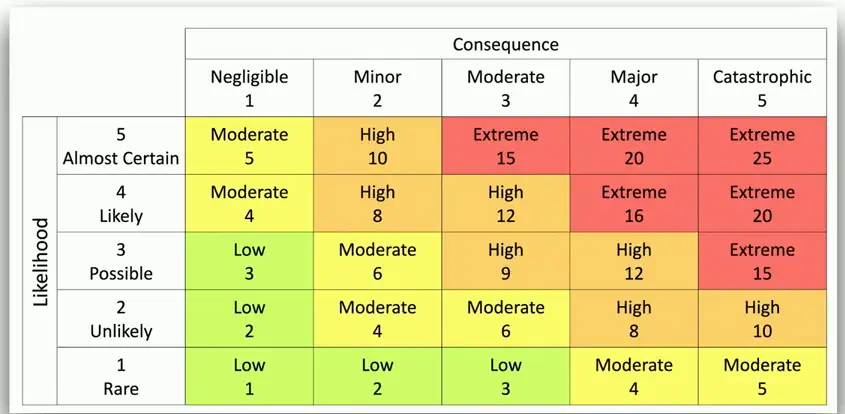
Likelihood and Probability
Risk likelihood
- A qualitative measurement of risk
- Rare, possible, almost certain, etc.
Risk probability
- A quantitative measurement of risk
- A statistical measurement
- Can be used based on historical performance
Often considered similar in scope
- Can be used interchangeably in casual conversation
Risk Appetite and Tolerance
Risk appetite
- A broad description of risk-taking deemed acceptable
- The amount of accepted risk before taking any action to reduce that risk
Risk appetite posture
- Qualitative description for readiness to take risk
- Conservative, neutral, and expansionary
Risk tolerance
- An acceptable variance (usually larger) from the risk appetite
Risk appetite example:
- A highway’s speed limit
- Government authorities have set the speed limit
- The limit is an acceptable balance between safety and convenience
Risk tolerance example:
- Drivers will be ticketed when the speed limit is violated
- Ticketing usually occurs well above the posted limit
- This tolerance can change with road conditions, weather, traffic, etc.
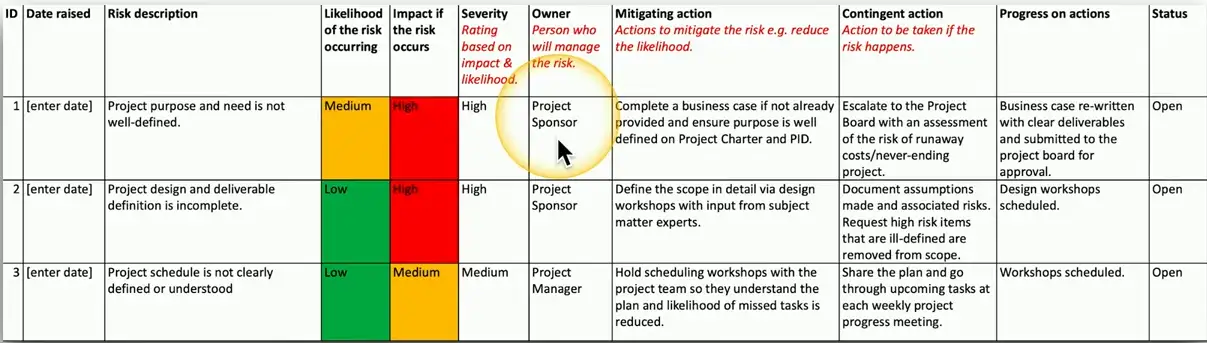
Risk Register
Every project has a plan, but also has risk
- Identify and document the risk associated with each step
- Apply possible solutions to the identified risks
- Monitor the results
Key risk indicators
- Identify risks that could impact the organization
Risk owners
- Each indicator is assigned someone to manage the risk
Risk threshold
- The cost of mitigation is at least equal to the value gained by mitigation
Risk Management Strategies
Accept with exemption
- A security policy or regulation cannot be followed
- May be based on available security controls, size of the organization, total assets, etc.
- Exemption may need approval
Accept with exception
- Internal security policies are not applied
- Monthly security updates must be applied within 3 calendar days
- The monthly updates cause a critical software package to crash
- An exception is made to the update timeframe
Avoid
- Stop participating in a high-risk activity
- This effectively removes the risk
Mitigate
- Decrease the risk level
- Invest in security systems
Risk Reporting
A formal document
- Identifies risk
- Detailed information for each risk
Usually created for senior management
- Make decisions regarding resources, budgeting, additional security tasks
Commonly includes critical and emerging risks
- The most important consideration
Business Impact Analysis
Recovery
Recovery time objective (RTO)
- Get up and running quickly
- Get back to a particular service level
- You’re not up and running until the database and web server are operational
- How long did that take?
Recovery point objective (RPO)
- How much data loss is acceptable?
- Bring the system back online; how far back does data go?
- The database is up, but only provides the last twelve months of data
Meantime to repair (MTTR)
- Average time required to fix an issue
- This includes time spent diagnosing the problem
- An important metric for determining the cost and time associated with unplanned outages
Mean time between failures (MTBF)
- The time between outages
- Can be used as a prediction or calculated based on historical performance
Total Uptime/Number of Breakdowns- Statistically plan for possible outages