Security Awareness
Security Awareness
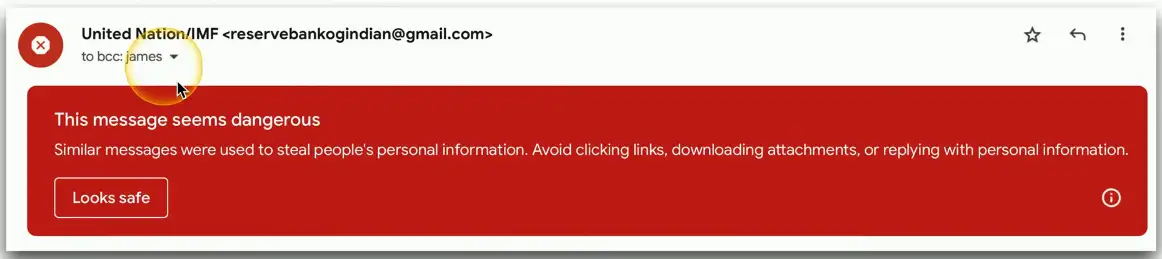
Phishing Campaigns
How many employees would click a link in a phishing email
- There’s way to find out
Many companies will perform their own phishing campaign
- Send a phishing email to your employees
An automated process
- Centralized reporting for incorrect clicks
- Users can receive immediate feedback and security training
- Some organizations will schedule in-person training
Recognize a phishing attempt
- Spelling and grammatical errors
- Domain name and email inconsistencies
- Unusual attachments
- Request for personal information
Tip
With the rise of Large language models, phishing campaigns has become more sophisticated and personalized.
Respond to reported suspicious messages
- Email filtering can get the worst offenders
- Never click a link in an email
- Never run an attachment from an email
- All organizations should have a process for reporting phishing
Anomalous Behavior Recognition
Risky behavior
- Modifying hosts file
- Replacing a core OS file
- Uploading sensitive files
Unexpected behavior
- Logon from another country
- Increase in data transfers
Unintentional behavior
- Typing the wrong domain name
- Misplacing USB drives
- Misconfiguring security settings
Reporting and Monitoring
Track and analyze security awareness metrics
- Automated
- Phishing click rates
- Password manager adoption, MFA use, password sharing
Initial
- First occurrence is an opportunity for user training
- Work towards avoiding the issue in the future
Recurring
- The value of long-term monitoring
- Identify high-frequency security issues
- Help users with multiple occurrences
Development
Create a Security Awareness team
- Determine roles for training, monitoring, policy creation, etc.
Establish a minimum awareness level
- Information delivery (emails, posters, notices, training)
- Depth of training based on job function
Integrate compliance mandates
- PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, etc.
Define metrics
- Assess the performance of security awareness programs
- Make updates in lower-performance areas
Execution
Create the training materials
- Provided to users in different forms
Document success measurements
- How will we know the awareness is working?
Identify the stakeholders
- Provide ongoing metrics and performance data
Deploy the training material
- Classroom training, posters, weekly emails, etc.
Track user training efforts
- Ongoing monitoring, usually with an automated reporting system
User Training
Security Awareness Training
Before providing access, train your users
- Detailed security requirements
Specialized training
- Each user role has unique security responsibilities
Also applies to third-parties
- Contractors, partners, suppliers
Detailed documentation and records
- Problems later can be severe for everyone
User Guidance and Training
Policy/handbooks
- Document all security requirements
- Provide access online in policy guidelines
- Reference the policies in the employee handbook
Situational awareness
- Users should always be looking for threats
- Software attacks: Email links, attachments, unusual URLs, text messages, etc.
- Physical Attacks: USB drives in a FedEx envelope, unlocked building doors, etc.
- Be ready for anything
Insider threat
- Difficult to guard against
- Add multiple approvals for critical processes
- Monitor files and systems as much as possible
Password management
- Many standards to choose from
- Guide users with standard requirements (length, complexity, etc.)
- This is often controlled using technology (Group Policy)
Removable media and cables
- Unknown USB drives can contain malware
- Unknown cables can be malicious
Social engineering
- Extensive and ongoing training
- The attackers are very good
- The users are your front line defense
Operational security
- View security from the attacker’s perspective
- Users need to identify sensitive data
- Keep the sensitive data private
Hybrid/remote work environments
- Working at home brings unusual security risks
- No access to family and friends
- Additional endpoint security
- Security policies for VPN access