Applying Security Principles
Secure Infrastructures
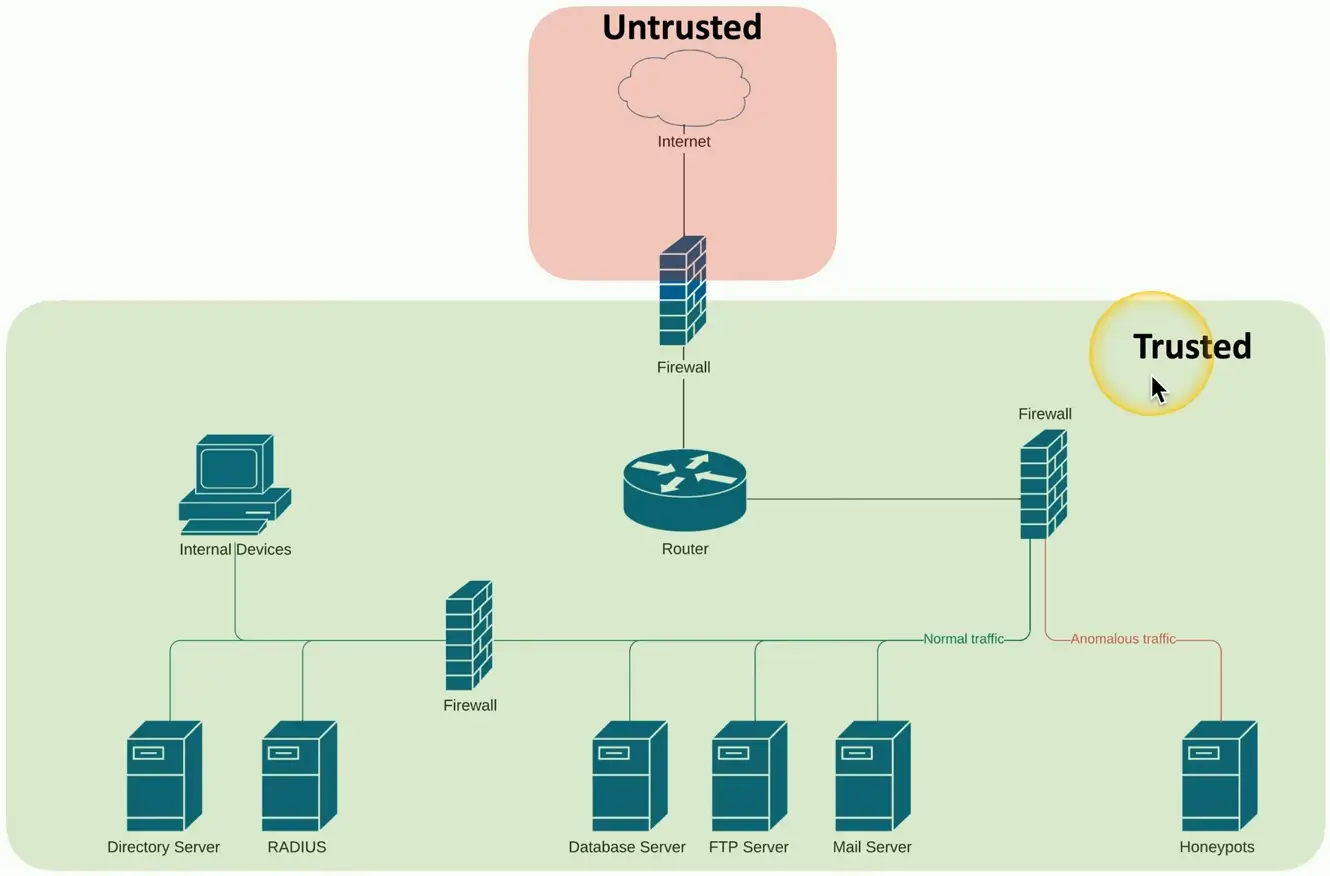
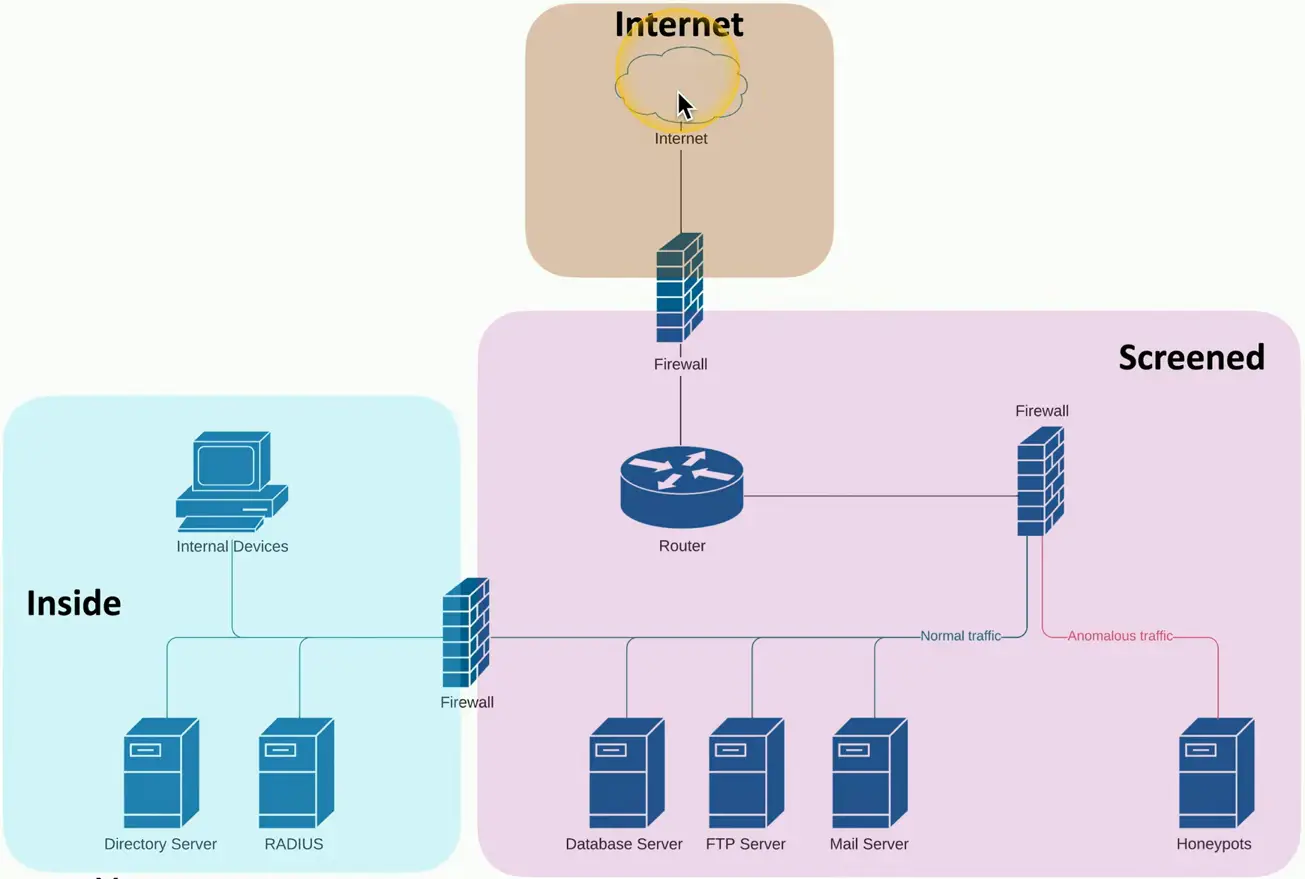
Device Placement
Every network is different
- There are often similarities
Firewalls
- Separate trusted from untrusted
- Provide additional security checks
Other services may require their own security technologies
- Honeypots, jump server, load balancers, sensors
Security Zone
Zone-based security technologies
- More flexible (and secure) than IP address ranges
Each area of the network is associated with a zone
- Trusted, untrusted
- Internal, external
- Inside, Internet, Servers, Databases, Screened
This simplifies security policies
- Trusted to Untrusted
- Untrusted to Screened
- Untrusted to Trusted
Attack Surface
How many ways into your home?
- Doors, windows, basements
Everything can be a vulnerability
- Application code
- Open ports
- Automated process
- Human error
Minimize the surface
- Audit the code
- Block ports on the firewall
- Monitor network traffic in real-time
Connectivity
Everything contributes to security
- Including the network connection
Secure network cabling
- Protect the physical drops
Application-level encryption
- The hard work has already been done
Network-level encryption
- IPsec tunnels, VPN connections
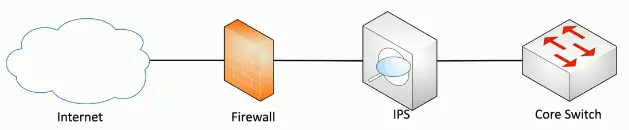
Intrusion Prevention
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
Intrusion Prevention System
- Watch network traffic
Intrusions
- Exploits against OSes, applications, etc.
- Buffer overflows, cross-site scripting, other vulnerabilities
Detection vs. Prevention
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS) — Alarm or alert
- Prevention — Stop it before it gets into the network
Failure Modes
We hope for 100% uptime
- This obviously isn’t realistic
- Eventually, something will break
Fail-open
- When a system fails, data continues to flow
Fail-closed
- When a system fails, data does not flow
Device Connections
Active monitoring
- System is connected inline
- Data can be blocked in real-time as it passes by
- Intrusion prevention is commonly active
Passive monitoring
- A copy of the network traffic is examined using a tap or port monitor
- Data cannot be blocked in real-time
- Intrusion detection is commonly passive
Active Monitoring
Malicious traffic is immediately identified
- Dropped at the IPS
- Doesn’t proceed through the network
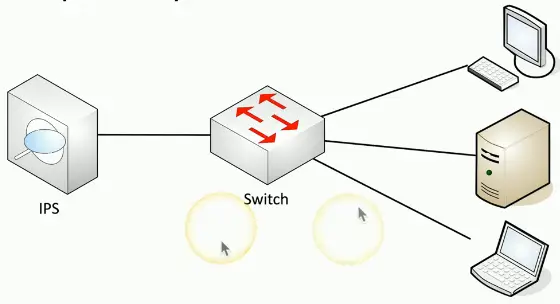
Passive Monitoring
Examine a copy of the traffic
- Port mirror (SPAN), network tap
No way to block (prevent) traffic
- Common with Intrusion Detection Systems
Network Appliances
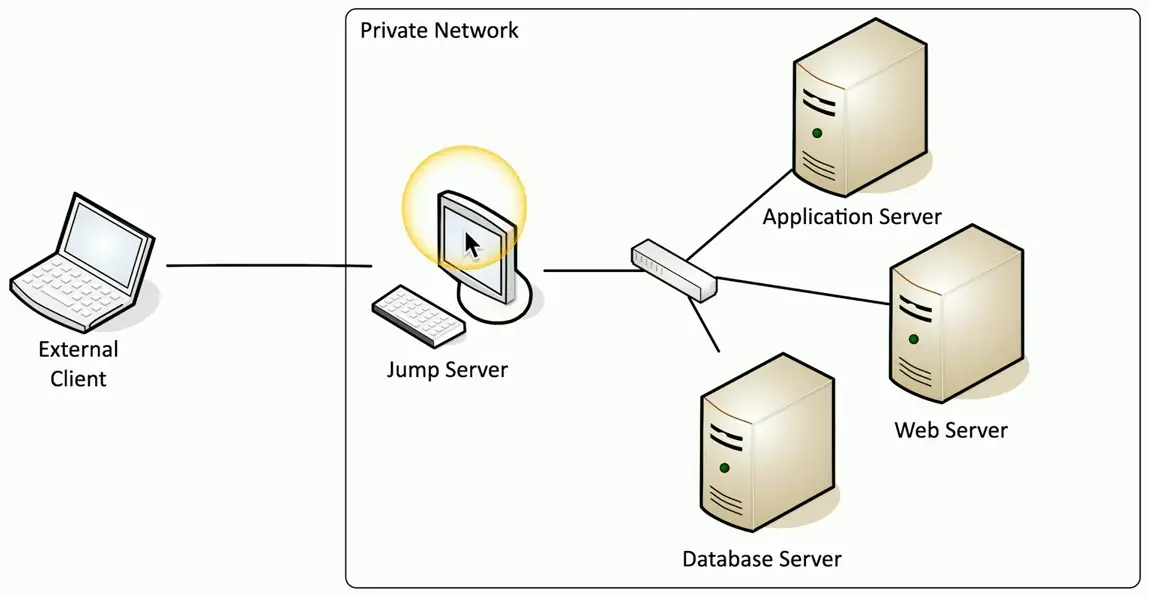
Jump Server
Access secure network zones
- Provides an access mechanism to a protected network
Highly-secured device
- Hardened and monitored
SSH/Tunnel/VPN to the jump server
- RDP, SSH, or jump from there
A significant security concern
- Compromise of the jump server is a significant breach
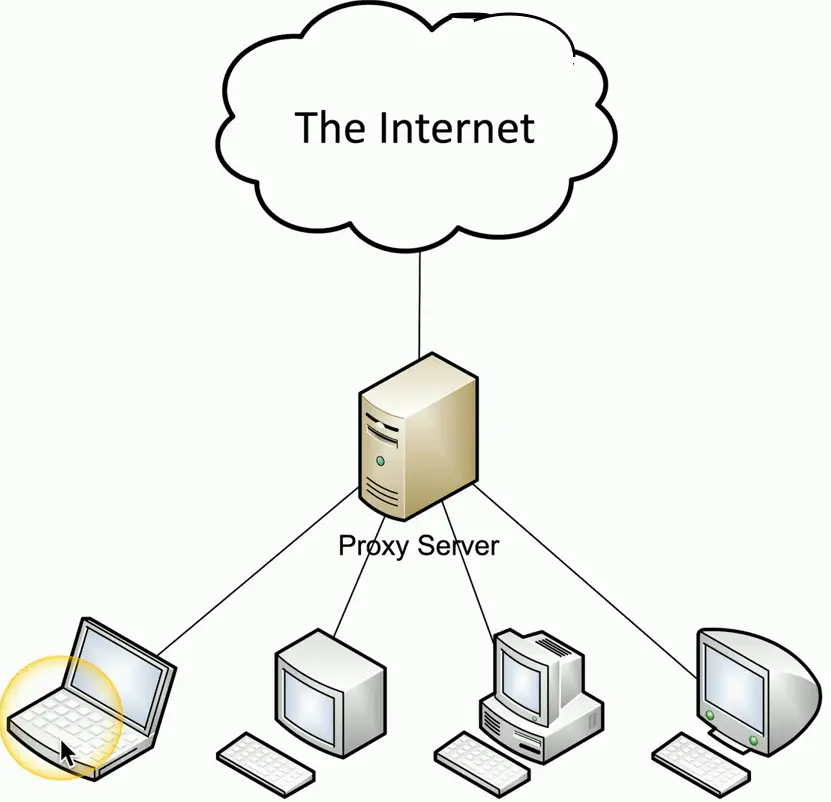
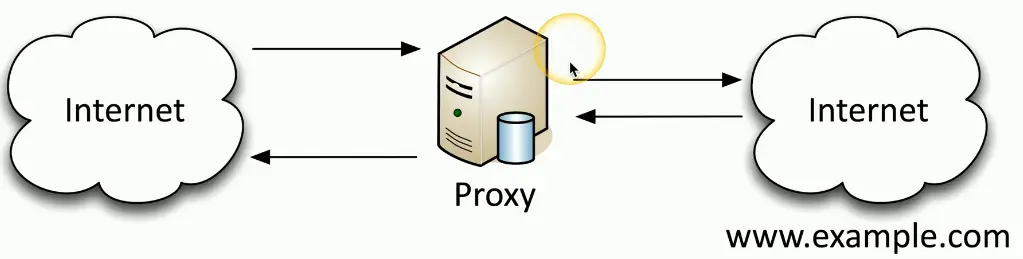
Proxies
- Sits between the users and the external network
- Receives the user requests and sends the request on their behalf (the proxy)
- Useful for caching information, access control, URL filtering, content scanning
- Applications may need to know how to use the proxy (explicit)
- Some proxies are invisible (transparent)
- Users don’t need to configure anything for the proxy to work on their end
Application Proxies
One of the simplest “proxies” is NAT
- A network level proxy
Most proxies in use are application proxies
- The proxy understands the way the application works
A proxy may only know one application
- HTTP
Many proxies are multipurpose proxies
- HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, etc.
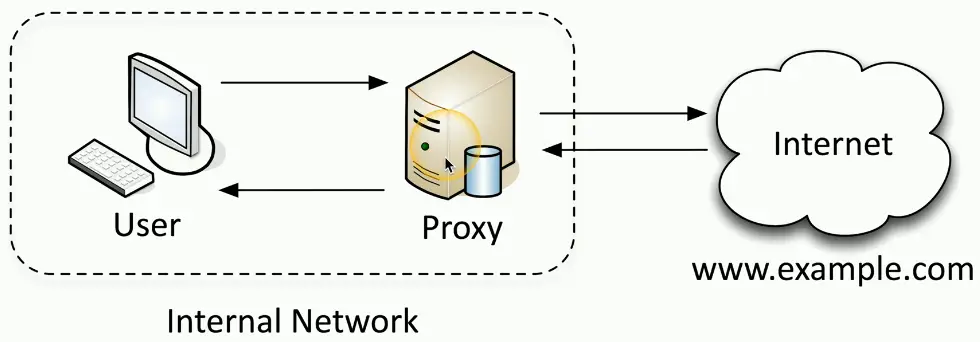
Forward Proxy
An “internal proxy”
- Commonly used to protect and control user access to the Internet
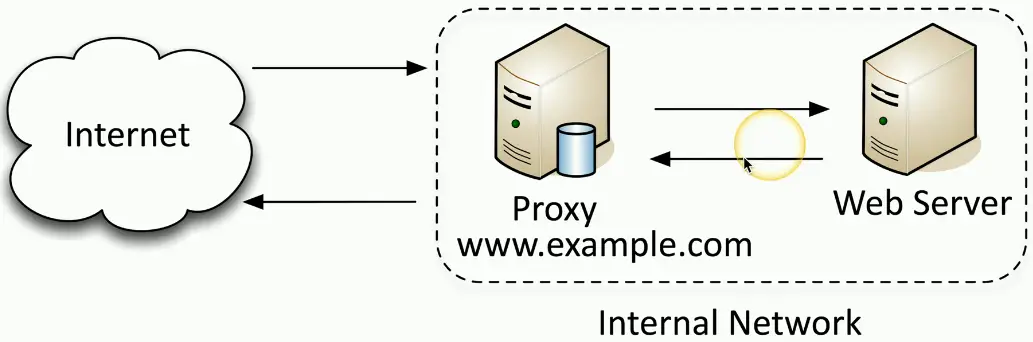
Reverse Proxy
Inbound traffic from the Internet to your internal service
Open Proxy
A third party, uncontrolled proxy
- Can be a significant security concern
- Often used to circumvent existing security controls
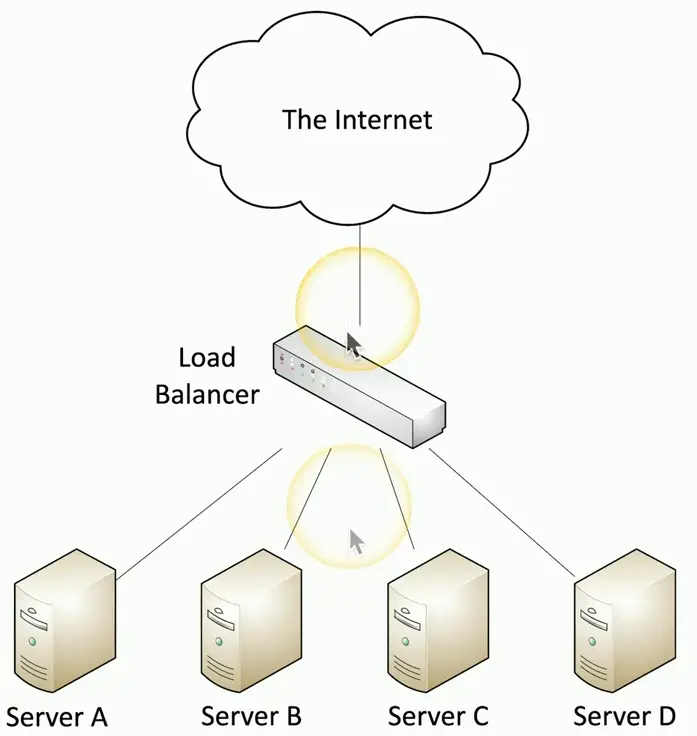
Balancing the Load
Distribute the load
- Multiple servers
- Invisible to the end-user
Large-scale implementations
- Web server farms, database farms
Fault tolerance
- Server outages have no effect
- Very fast convergence
Active/active Load Balancing
Configurable load
- Manage across servers
TCP offload
- Protocol overhead
SSL offload
- Encryption/Decryption
Caching
- Fast response
Prioritization
- QoS
Content Switching
- Application-centric balancing
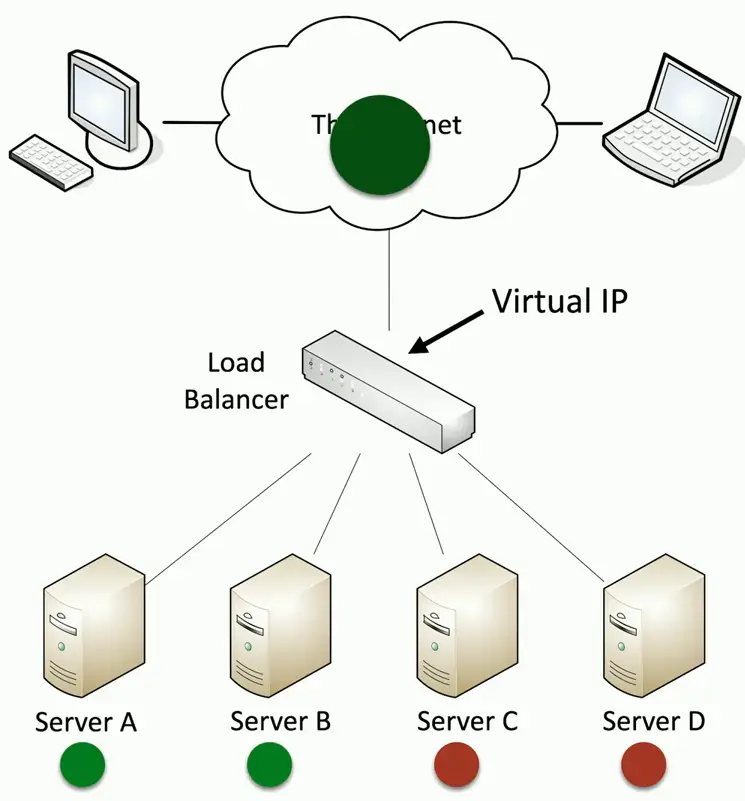
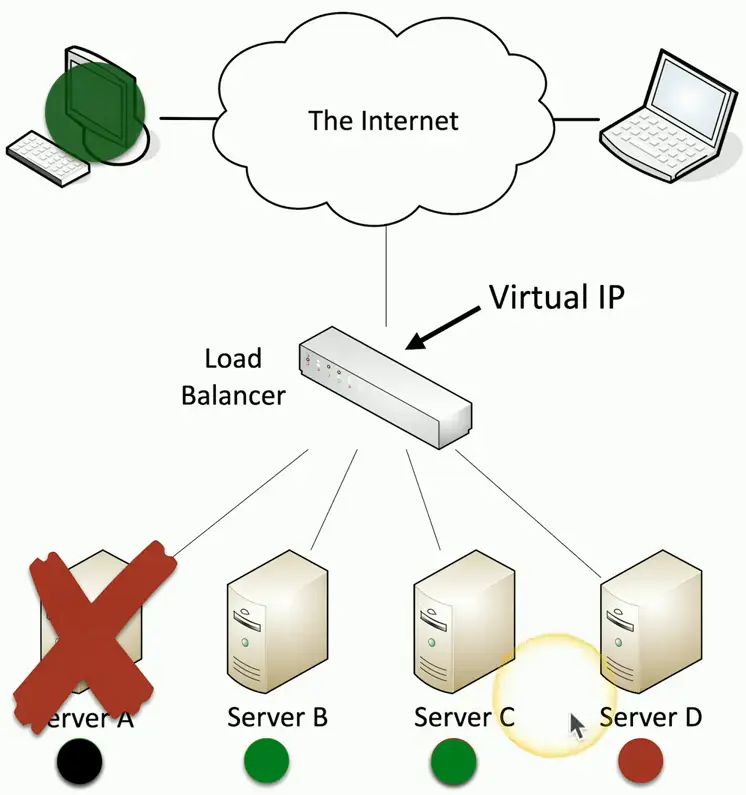
Active/Passive Load Balancing
Some servers are active
- Others are on standby
If an active server fails, the passive server takes its place
Sensors and Collectors
Aggregate information from network devices
- Built-in sensors, separate devices
- Integrated into switches, routers, servers, firewalls, etc.
Sensors
- Intrusion prevention systems, firewall logs, authentication logs, web server access logs, database transaction logs, email logs
Collectors
- Proprietary consoles (IPS, firewall), SIEM consoles, syslog serves
- Many SIEMs include a correlation engine to compare diverse sensor data
Port Security
We have created many authentication methods through the years
- A network administrator has many choices
Use a username and password
- Other factors can be included
Commonly used on wireless networks
- Also works on wired networks
EAP
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
- An authentication framework
Many ways to authenticate based on RFC standards
- Manufacturers can build their own EAP methods
EAP integrates with 802.1X
- Prevents access to the network until the authentication succeeds
IEEE 802.1X
IEEE 802.1X
- Port-based Network Access Control (NAC)
- You don’t get access to the network until you authenticate
EAP integrates with 802.1X
- Extensible Authentication Protocol
- 802.1X prevents access to the network until the authentication succeeds
Used in conjunction with an authentication database
- RADIUS, LDAP, TACACS+, Kerberos, etc.
IEEE 802.1X and EAP
- Supplicant — The client
- Authenticator — The device that provides access
- Authentication server — Validates the client credentials
Firewall Types
The Universal Security Control
Standard issue
- Home, office, and in your OS
Control the flow of network traffic
- Everything passes through the firewall
Corporate control of outbound and inbound data
- Sensitive materials
Control of inappropriate content
- Not safe for work, parental controls
Protection against evil
- Anti-virus, anti-malware
Network-based Firewalls
Filter traffic by port number or application
- OSI layer 4 vs. OSI layer 7
- Traditional vs. NGFW firewalls
Encrypt traffic
- VPN between sites
Most firewalls can be a layer 3 devices (routers)
- Often sits on the ingresses/egress of the network
- Network Address Translation (NAT) functionality
- Authenticate dynamic routing communication
UTM/ All-in-one Security Appliance
- Unified Threat Management (UTM)/Web Security gateway
- URL filter/Content inspection
- Malware inspection
- Spam filter
- CSU (Channel Service Unit)/DSU (Data Service Unit)
- Router, Switch
- Firewall
- IDS/IPS
- Bandwidth shaper
- VPN endpoint
[! Warning] Using all features at once, will slow down the network. So enable those only you need.
Next-generation Firewall (NGFW)
The OSI Application Layer
- All data in every packet
Can be called different names
- Application layer gateway
- Stateful multilayer inspection
- Deep packet inspection
Requires some advanced decodes
- Every packet must be analyzed and categorized before a security decision is determined
Network-based Firewalls
- Control traffic flows based on the application
- Microsoft SQL server, Twitter/X, YouTube
Intrusion Prevention Systems
- Identify the application
- Apply application-specific vulnerability signatures to the traffic
Content filtering
- URL filters
- Control website traffic by category
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Not like a “normal” firewall
- Applies rules to HTTP/HTTPS conversations
Allow or deny based on expected input
- Unexpected input is a common method of exploiting an application
SQL injection
- Add your own commands to an application’s SQL query
A major focus of Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
Secure Communication
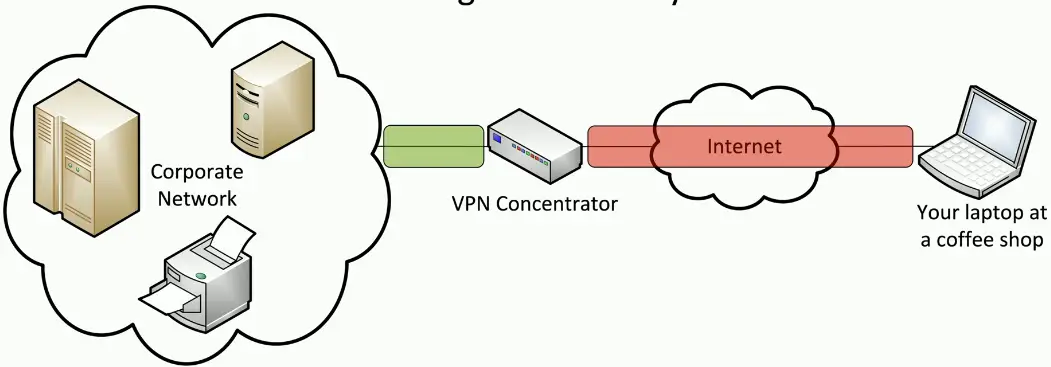
VPN
Virtual Private Networks
- Encrypted (private) data transversing a public network
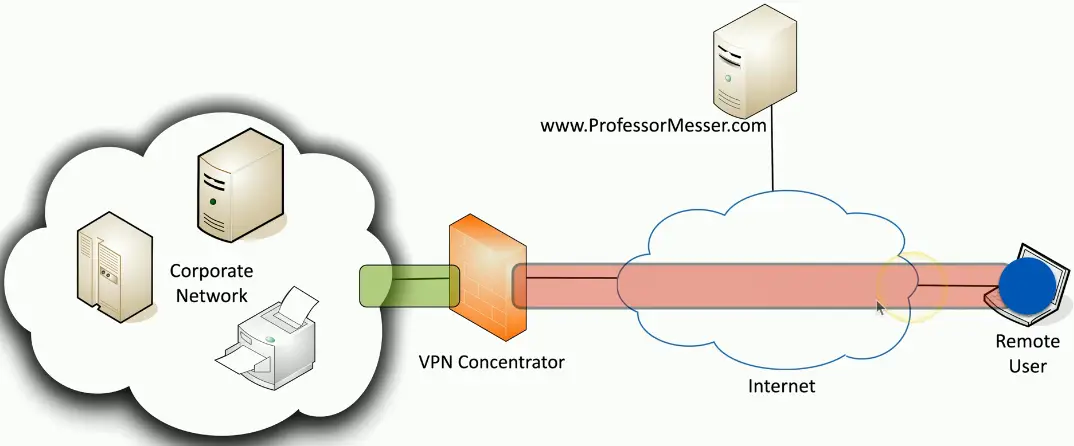
Concentrator
- Encryption/decryption access device
- Often integrated into a firewall
Many deployment options
- Specialized cryptographic hardware
- Software-based options available
Used with client software
- Sometimes built into the OS
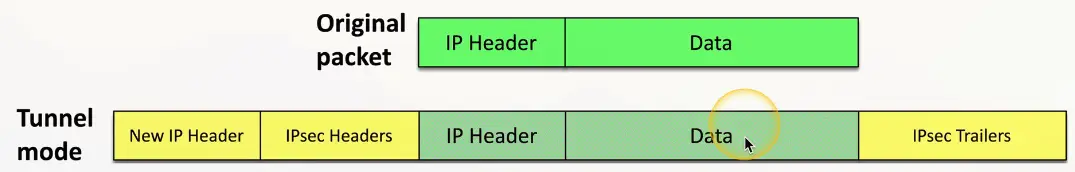
Encrypted Tunnel
Keep data private across the public internet
- Encryption is the key
Encrypt your data
- Add new headers and trailers
Decrypt on the other side
- Original data is delivered
SSL/TLS VPN (Secure Sockets Layer VPN)
Uses common SSL/TLS protocol (TCP/443)
- (Almost) No firewall issues
No big VPN clients
- Usually remote access communication
Authenticate users
- No requirement for digital certificates or shared passwords (like IPSec)
Can be run from a browser or from a (usually light) VPN client
- Across many OSes
On-demand access from a remote device
- Software connects to a VPN concentrator
Some software can be configured as always-on
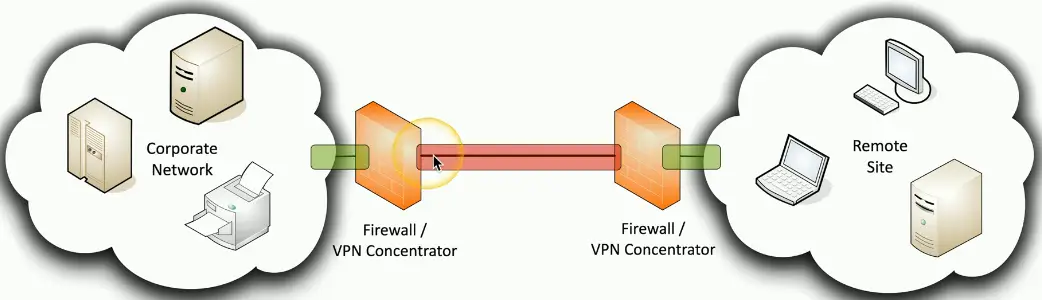
Site-to-site IPsec VPN
Always-on
- Or almost always
Firewalls often act as VPN concentrators
- Probably already have firewalls in place
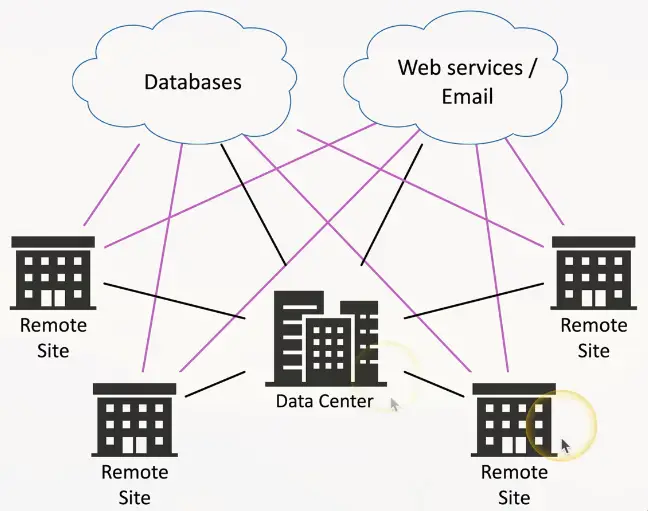
SD-WAN
Software Defined Networking in a Wide Area Network
- A WAN built for the cloud
The data center used to be in one place
- The cloud has changed everything
Cloud-based applications communicate directly to the cloud
- No need to hop through a central point
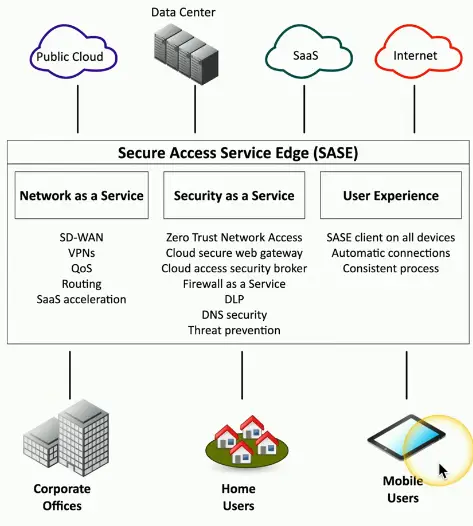
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
Update secure access for cloud services
- Securely connect from different locations
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
- A “next generation” VPN
Security technologies are in the cloud
- Located close to existing cloud services
SASE clients on all device
- Streamlined and automatic
Selection of Effective Controls
Many security options
- Selecting the right choice can be challenging
VPN
- SSL/TLS VPN for user access
- IPsec tunnels for site-to-site access
SD-WAN
- Manage the network connectivity to the cloud
- Does not adequately address security concerns
SASE
- A complete network and security solution
- Requires planning and implementation