Transmission Media
Wireless Networking
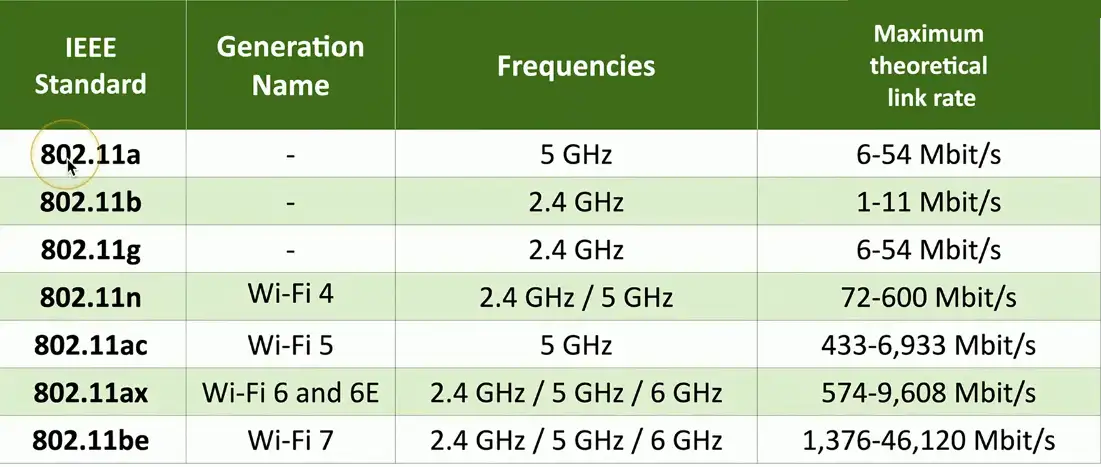
Wireless Standards
Wireless networking (802.11)
- Managed by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Many updates over time
- Check with IEEE for the latest
The Wi-Fi trademark
- Wi-Fi Alliance handles interoperability testing
Modern standards have a more marketable name
- For example, 802.11ax is Wi-Fi 6
4G and LTE
Long Term Evolution (LTE)
- A “4G” technology
- converged standard (GSM and CDMA providers)
- Based on GSM and EDGE (Enhanced Data Rated for GSM Evolution)
- Standard supports download rates of 150 Mbit/s
LTE Advanced (LTE-A)
- Standard supports download rates of 300 Mbit/s
5G
Fifth generation cellular networking
- Launched worldwide in 2020
Significant performance improvements
- At higher frequencies
- Eventually 10 gigabits per second
- Slower speeds from 100-900 Mbit/s
Significant IoT impact
- Bandwidth becomes less of a constraint
- Larger data transfers
- Faster monitoring and notification
- Additional cloud processing
Satellite Networking
Communication to a satellite
- Non-terrestrial communication
High cost relative to terrestrial networking
- 100 Mbit/s down, 5 Mbit/s up are common
- Remote sites, difficult-to-network sites
Relatively high latency
- 250 ms up, 250 ms down
- Starlink advertises 40 ms and is working on 20 ms
High frequencies — 2 GHz
- Line of sight, rain fade
Ethernet Standards
Ethernet
The most popular networking technology in the world
- Standard, common, nearly universal
Many types of Ethernet
- Speeds, cabling, connectors, equipment
Modern Ethernet uses twisted pair copper or fiber
- The standard defines the media
IEEE Ethernet Standards
The IEEE 802.3 committee
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
- All types of standards of Ethernet
- Copper and fiber
| IEEE Standard | Description | Media | Network Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000BASE-T | Gigabit Ethernet | Copper | 1 gigabit per second |
| 10GBASE-T | 10 Gigabit Ethernet | Copper | 10 gigabits per second |
| 1000BASE-SX | Gigabit Ethernet | Fiber | 1 gigabit per second |
Deciphering the Standard
Speed signal, and media
- All contained in the standard name, i.e., 1000BASE-T
The number is related to the network speed
- 1000 is commonly 1,000 megabits per second (or one gigabit/sec)
- 10G would be 10 gigabits per second
BASE (baseband)
- Single frequency using the entire medium
- Broadband uses many frequencies, sharing the medium
Media type
- T is twisted pair copper, F is fiber
- SX would be short wavelength light
Optical Fiber
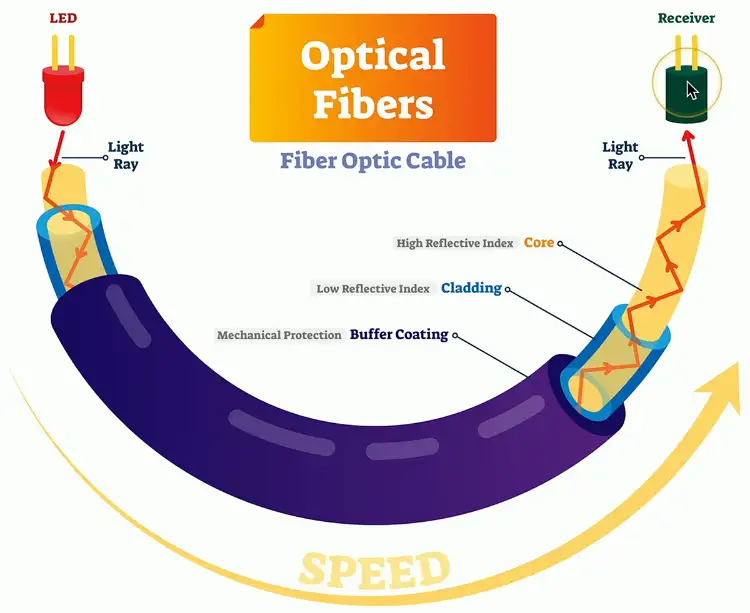
Fiber Communication
Transmission by light
- The visible spectrum
No RF signal
- Very difficult to monitor or tap
Signal slow to degrade
- Transmission over long distances
Immune to radio interference
- There’s no RF
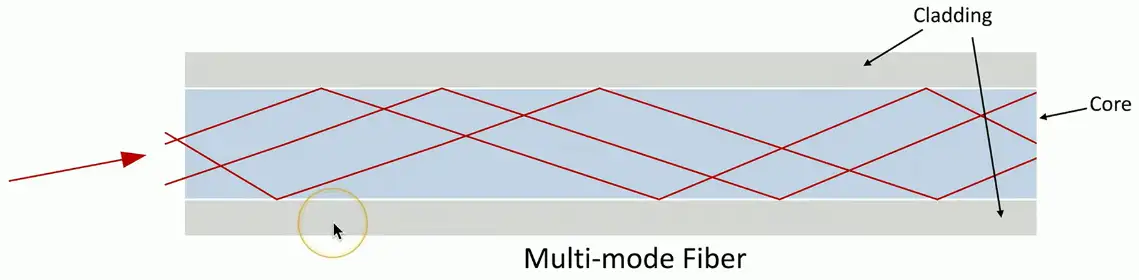
Multimode fiber
Short-range communication
- Up to 2 km
Inexpensive light source
- i.e., LED
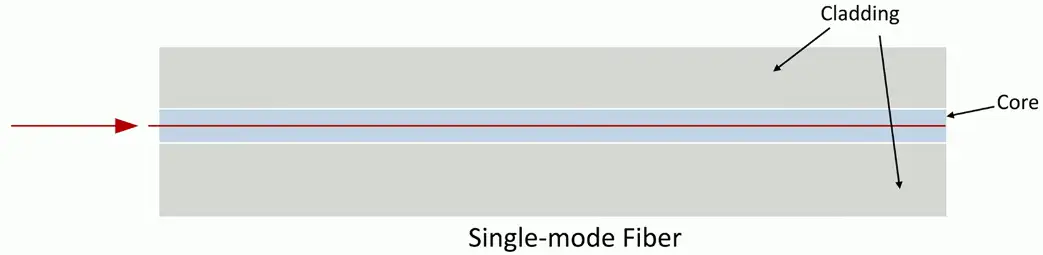
Single-mode Fiber
Long-range communication
- Up to 100 km without processing
Expensive light source
- Laser beams
Copper Cabling
The importance of cable
Fundamental to network communication
- Incredibly important foundation
Usually only get one good opportunity at building your cabling infrastructure
- Make it good!
The vast majority of wireless communication uses cables
- Everything eventually touches a cable
Twisted pair copper cabling
Balanced pair operation
- Two wires with equal and opposite signals
- Transmit+, Transmit-/Receive+, Receive-
The twist is the secret!
- Keep single wire constantly moving away from the interference
- The opposite signals are compared on the other end
Pairs in the same cable have different twist rates
Cable Speeds
Cables don’t have a speed
- The copper just sits there
Electrical signals are sent over copper cable
- The signal encoding determines the data transfer rate
A cable must be manufactured to specific standards
- IEEE 802.3 Ethernet standards determine the cable type
Cable standards are described as a “category” of cable
- Category 6, Category 7, etc.
- Check the IEEE standard to determine the minimum cable category
- The minimum cable category for 1000BASE-T is Category 5
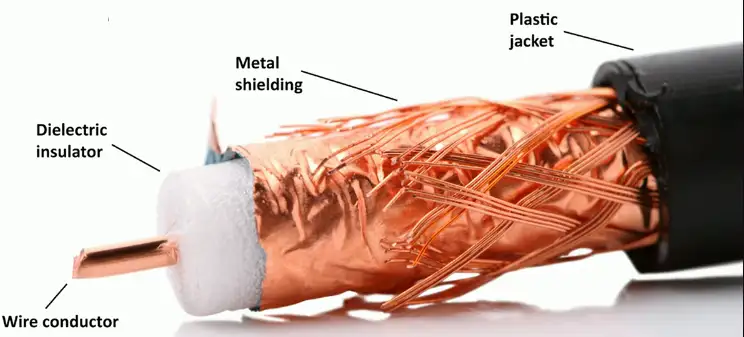
Coaxial Cables
Two or more forms share a common axis
RG-6 used in television/digital cable
- And high speed Internet over cable
Twinaxial Cable
Two inner conductors
- Twinax
Common on 10 Gigabit Ethernet SFP+ cables
- Full duplex
- Five meters
- Low cost
- Low latency compared to twisted pair
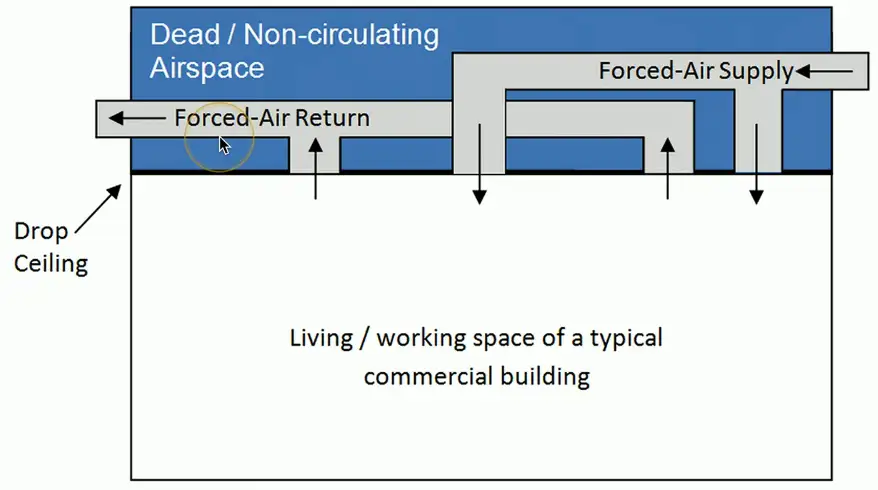
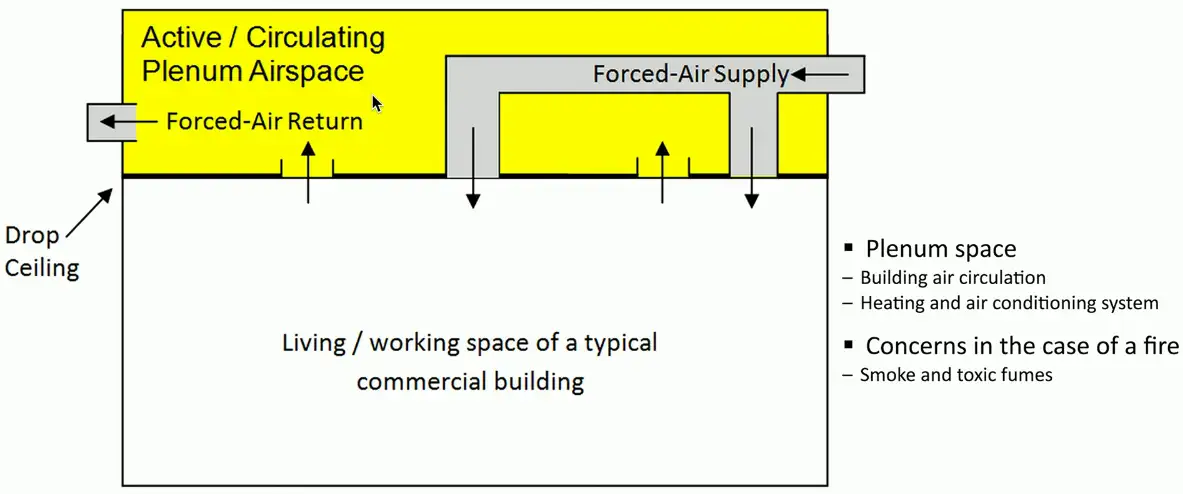
Plenum space
No Plenum
Plenum
Plenum-rated Cable
Traditional cable jacket
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Fire-rated cable jacket
- Fluorinated ethylene polymer (FEP) or low-smoke polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Plenum-rated cable may not be flexible
- May not have the same bend radius
Worst-case planning
- Used in plenum and risers
- Important concerns for any structure
Network Transceivers
Transmitter and receiver
- Usually in a single component
Provides a modular interface
- Add the transceiver that matches your network
Many types
- Ethernet or Fiber Channel
- Not compatible with each other
Different media types
- Fiber and copper
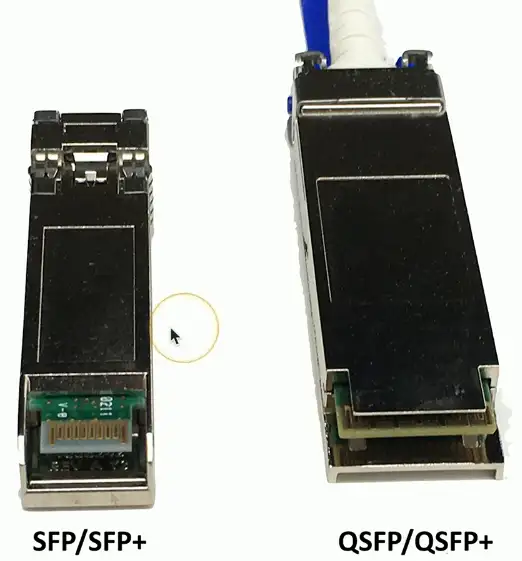
SFP and SFP+
Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP)
- Commonly used to provide 1 Gbit/s fiber
- 1 Gbit/s RJ45 SFPs also available
Enhanced Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP+)
- Exactly the same physical size as SFPs
- Supports data rates up to 16 Gbit/s
- Common with 10 Gigabit Ethernet
QSFP
Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable
- 4-channel SFP = Four 1 Gbit/s = 4 Gbit/s
- QSFP+ is four-channel SFP+ = Four 10 Gbit/sec = 40 Gbit/sec
Combine four SFPs into a single transceiver
- Cost savings in fiber and equipment
Transceiver Comparison
Fiber Connectors
SC — Subscriber Connector
Not actually an abbreviation
- We’ve created our own names
- Square Connector
- Standard Connector
Pushes on to lock
- Pull connector to unlock
A popular fiber connector
- Common in many data centers
Two SC connectors are combined in one.
LC — Local Connector
Another popular fiber type
- Smaller and more compact connector
Locks in place with a clip
- Press to release
Other names
- Lucent Connector
- Little Connector
Two LC connectors are combined here in pair.
ST — Straight TIP
Bayonet connector
- Stick and Twist
Push on and turn
- Locks in place
- Turn to unlock
MPO — Multi-fiber Push On
Twelve fibers in a single connector
- Save space and manage one cable
Push to lock in place
- Pull connector to unlock
May also see the MTP abbreviation
- A Corning brand
- The MTP MPO connector
Copper Connectors
RJ11 Connector
Registered Jack type 11
- 6 position, 2 conductor (6P2C)
Telephone & DSL connection
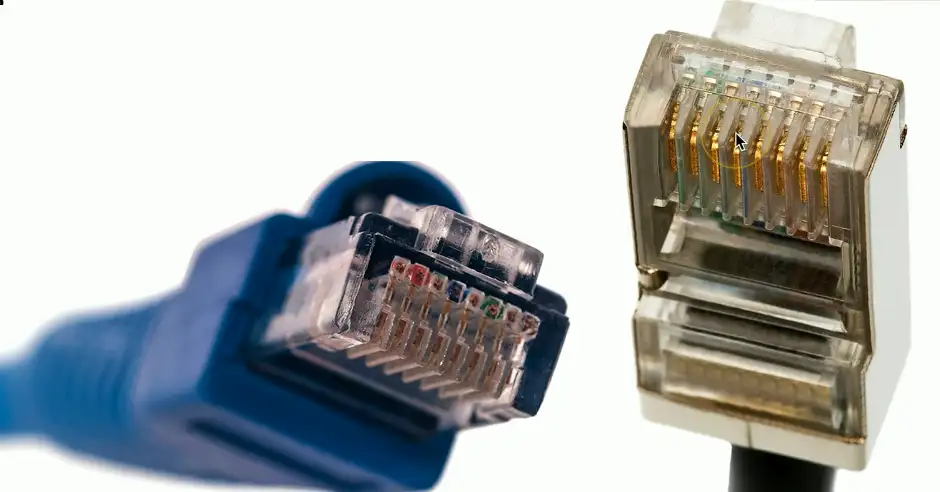
RJ45 Connector
Registered Jack type 45
8 positions, 8 conductors (8P8C)
- Modular connector
- Ethernet
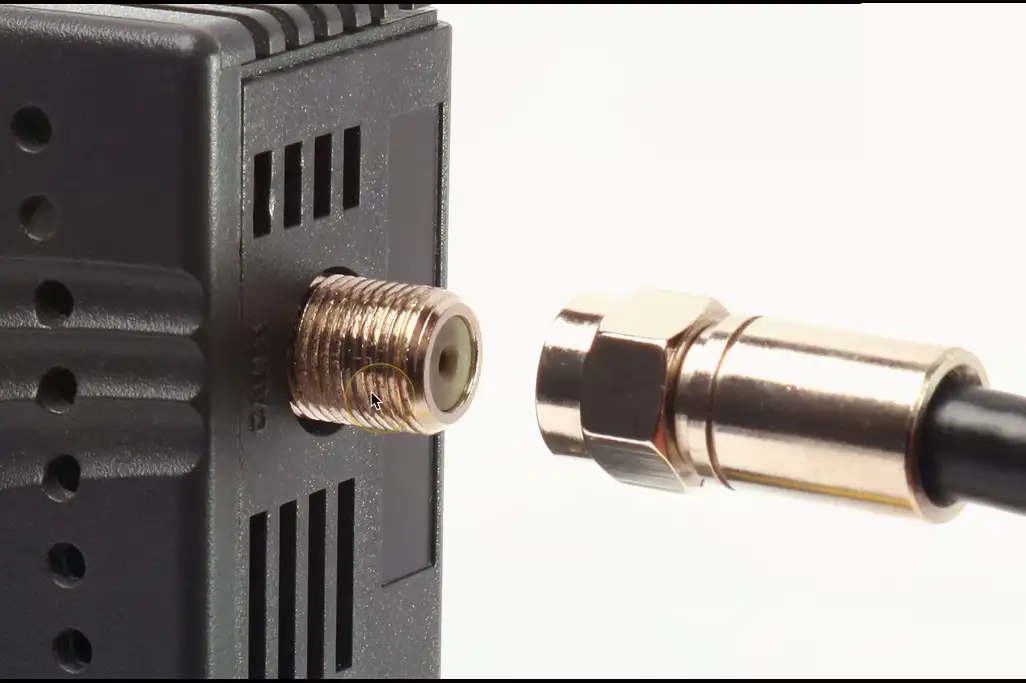
F-connector
Coaxial cable
- Standard connector type
- Threaded connector
Cable television infrastructure
- Cable modem
- DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification)
BNC Connector
Bayonet Neil-Concelman
- Paul Neil (Bell Labs) and Carl Concelman
Another common coaxial cable connector
- Common with twinax and DS3 WAN links
- Video connections
Secure connections
- Twist and lock in place