The Cloud
Designing the Cloud
On-demand computing power
- Click a button
Elasticity
- Scale up or down as needed
Applications also scale
- Scalability for large implementations
- Access from anywhere
Multitenancy
- Many clients are using the same cloud infrastructure
Virtual Networks
Server farm with 100 individual computers
- It’s a big farm
All servers are connected with enterprise switches and routers
- With redundancy
Migrate 100 physical servers to one physical server
- With 100 virtual servers inside
What happens to the network?
Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
Replace physical network devices with virtual versions
- Manage from the hypervisor
Same functionality as a physical device
- Routing, switching, load balancing, firewalls, etc.
Quickly and easily deploy network functions
- Click and deploy from the hypervisor
Many deployment options
- Virtual machine, container, fault tolerance, etc.
Connecting to the Cloud
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- A pool of resources created in a public cloud
Common to create many VPCs
- Many applications clouds
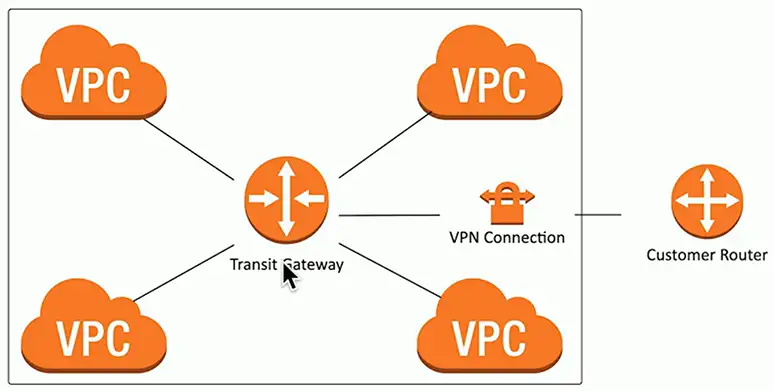
Connect VPCs with a transit gateway
- And users to VPCs
- A “cloud router”
Now make it secure
- VPCs are commonly on different IP subnets
- Connecting to the cloud is often through a VPN
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
- Site-to-site VPN through the Internet
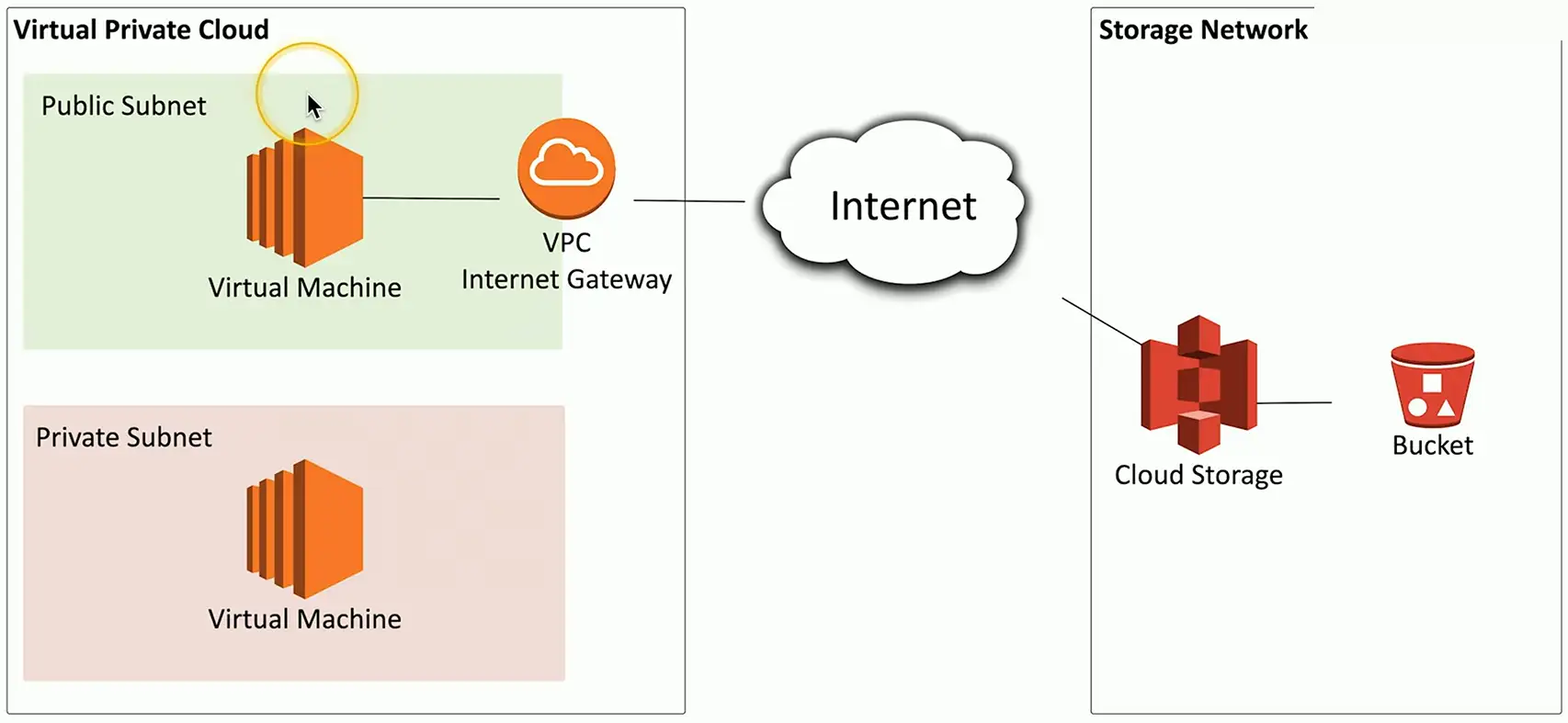
Virtual Private Cloud Gateway/Internet gateway
- Connects users on the Internet
VPC NAT gateway
- Network address translation
- Private cloud subnets connect to external resources
- External resources cannot access the private cloud
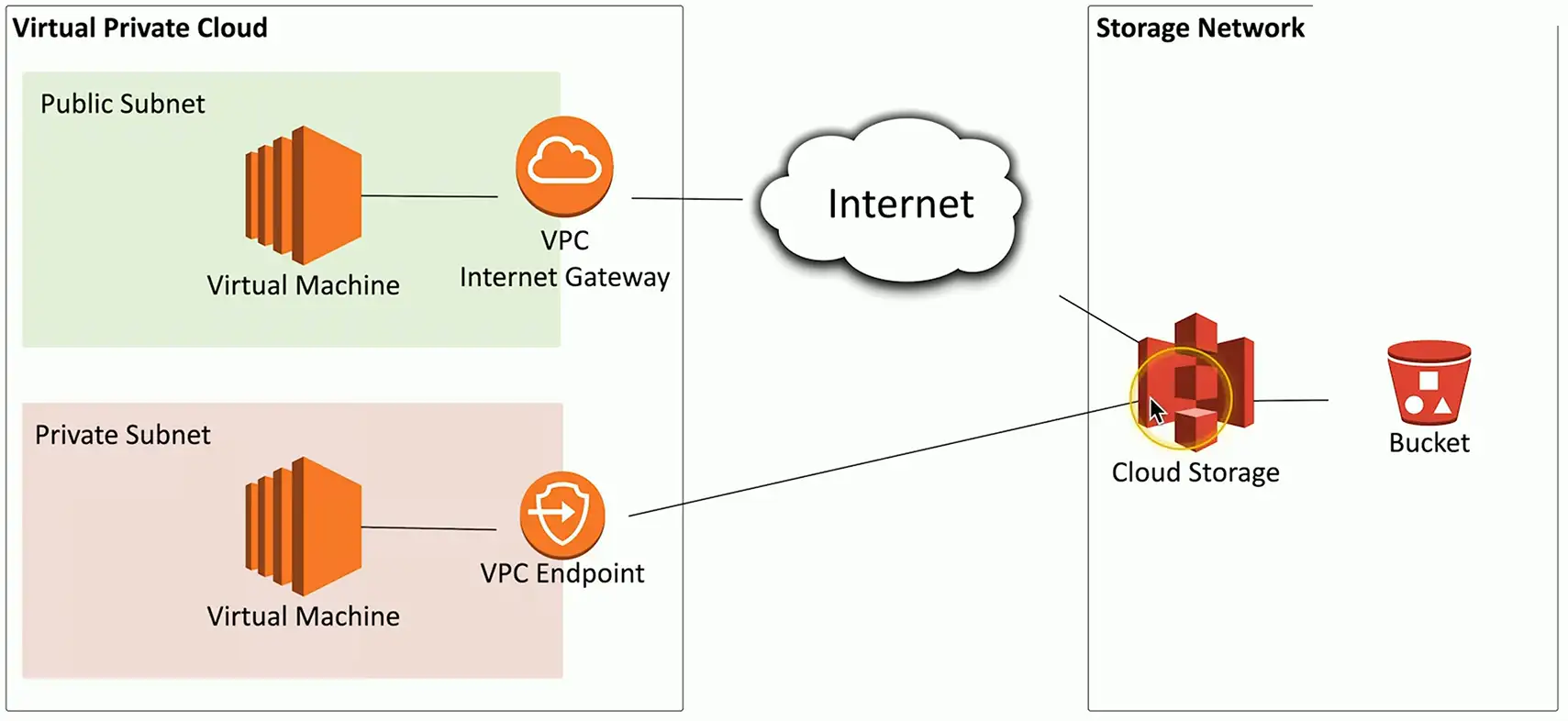
VPC Endpoint
- Direct connection between cloud provider networks
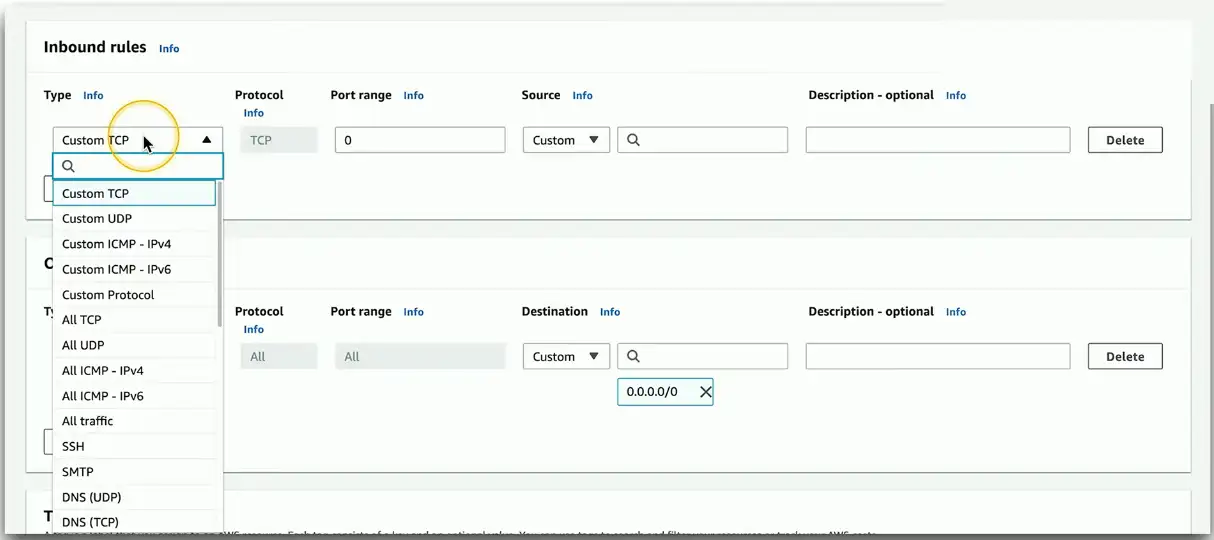
Security groups and lists
A firewall for the cloud
- Control inbound and outbound traffic flows
Layer 4 port number
- TCP or UDP port
Layer 3 address
- Individual addresses
- CIDR block notation
- IPv4 or IPv6
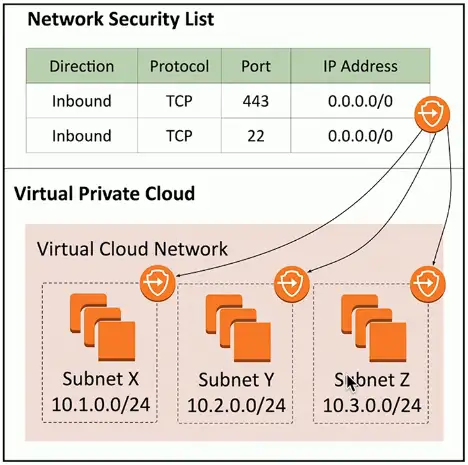
Network Security List
Assign a security rule to an entire IP subnet
- Applies to all devices in the subnet
Very broad
- Can become difficult to manage
- Not all devices in a subnet have the same security posture
More granularity may be needed
- Broad rules may not provide the right level of security
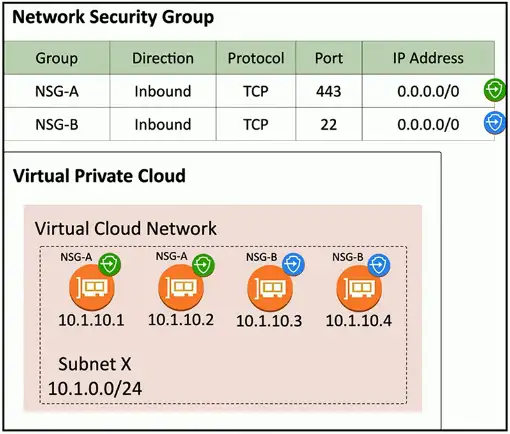
Network Security Group
Assign a security rule to a specific virtual NIC (VNIC)
- Applies to specific devices and network connections
More granular than network security lists
- Different rules for devices in the same IP subnet
Better control and granularity
- The best practice for cloud security rules
Cloud Models
Public
- Available to everyone over the Internet
Private
- Your own virtualized local data center
Hybrid
- A mix of public and private
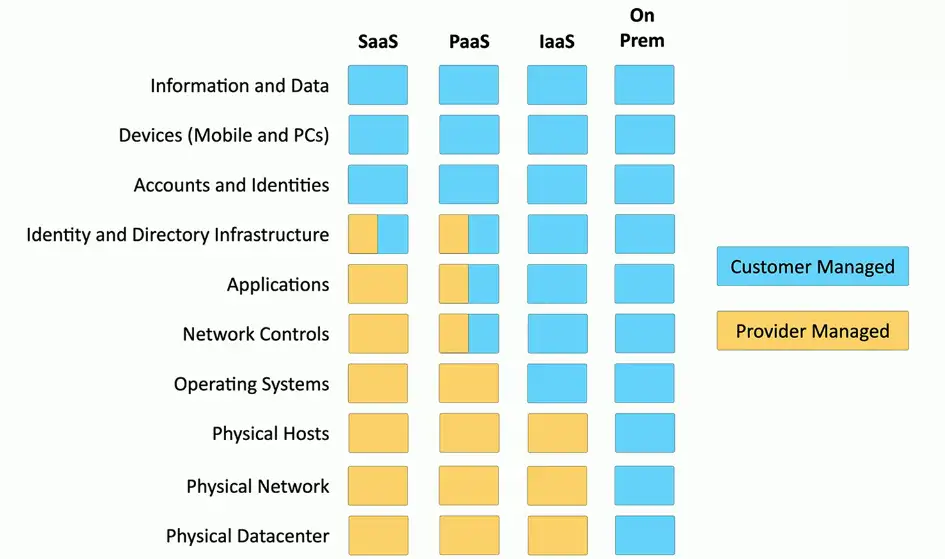
Software as a Service (SaaS)
On-demand software
- No local installation
- Why your own email distribution? Or payroll?
Central management of data and applications
- Your data is out there
A complete application offering
- No development work required
- Google Mail, Office 365
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Sometimes called Hardware as a Service (HaaS)
- Outsource your equipment
You’re still responsible for the management
- And for the security
Your data is out there, but more within your control
Web server providers
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
No servers, no software, no maintenance team, no HVAC
- Someone else handles the platform, you handle the development
You don’t have direct control of the data, people, or infrastructure
- Trained security professionals are watching your stuff
- Choose carefully
Put the building blocks together
- Develop your app from what’s available on the platform
- https://SalesForce.com