Tools and Protocols
Software Tools
Protocol Analyzers
Solve complex application issues
- Get into the details
Gathers frames on the network
- Or in the air
- Sometimes built into the device
View traffic patterns
- Identify unknown traffic
- Verify packet filtering and security controls
Large scale storage
- Big data analytics
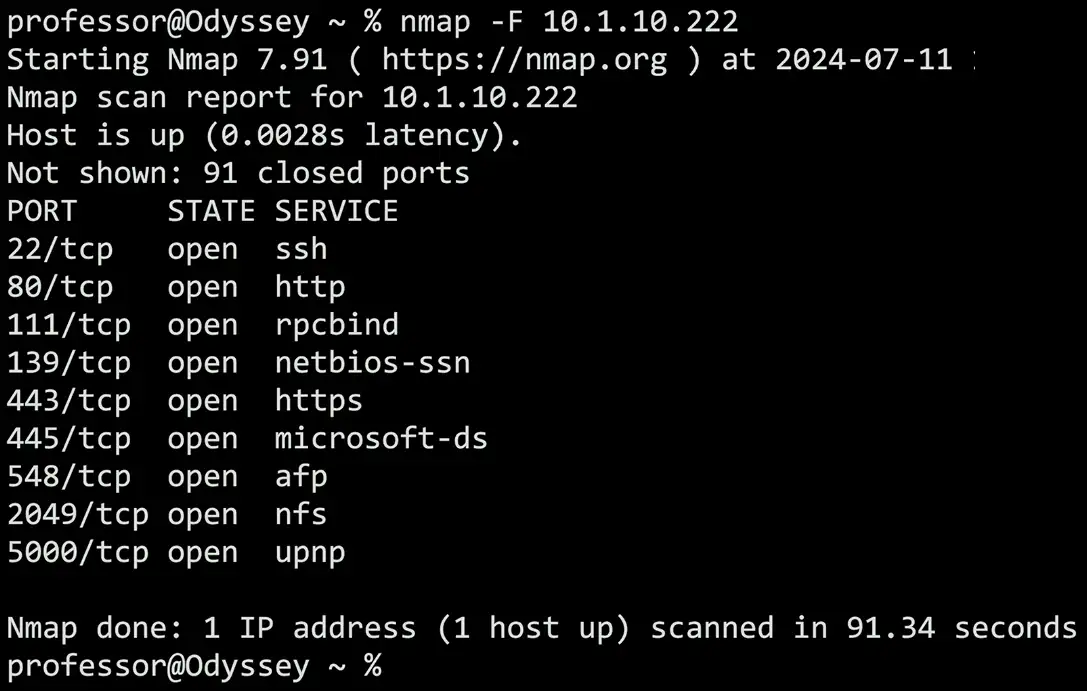
Nmap
Network mapper
- Find and learn more about network devices
Port scan
- Find devices and identify open ports
Operating system scan
- Discover the OS without logging in to a device
Service scan
- What service is available on a device? Name, version, details
Additional scripts
- Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE) — extend capabilities, vulnerability scans
Active — scan for IP addresses and open ports
- And OSes, services, etc.
Pick a range of IP addresses
- See who responds to the scan
Visually map the network
- Gather information on each device
- IP, OS, services, etc.
Rogue system detection
- It’s difficult to hide from a layer 2 ARP
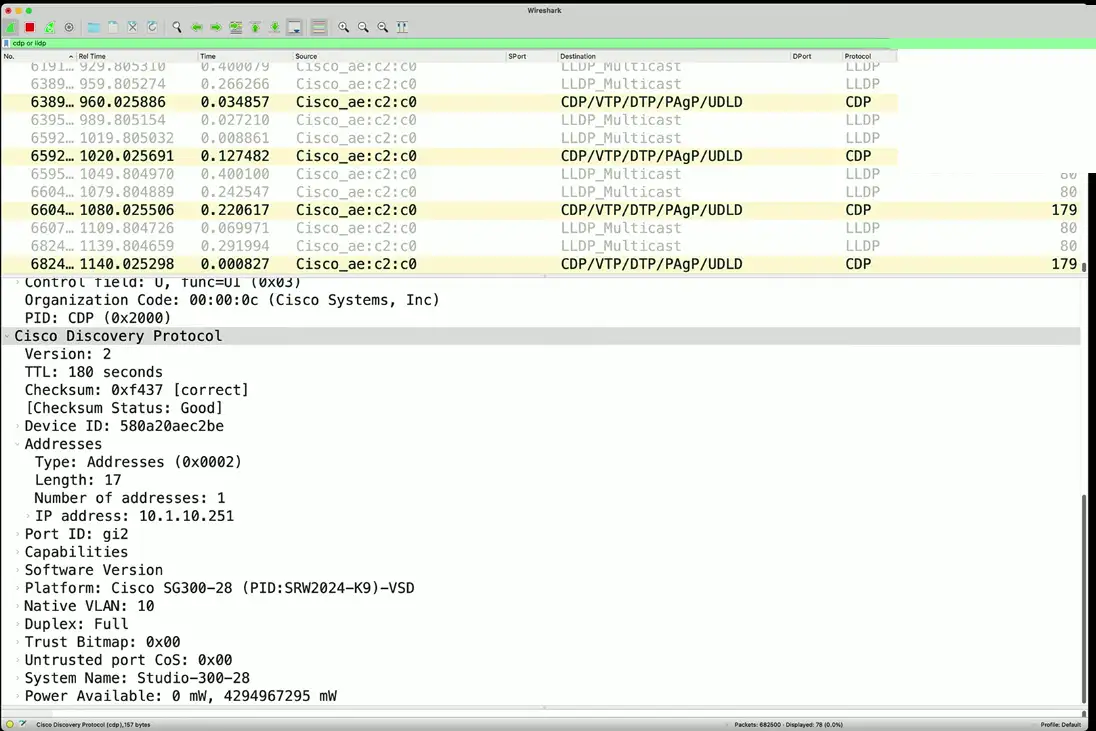
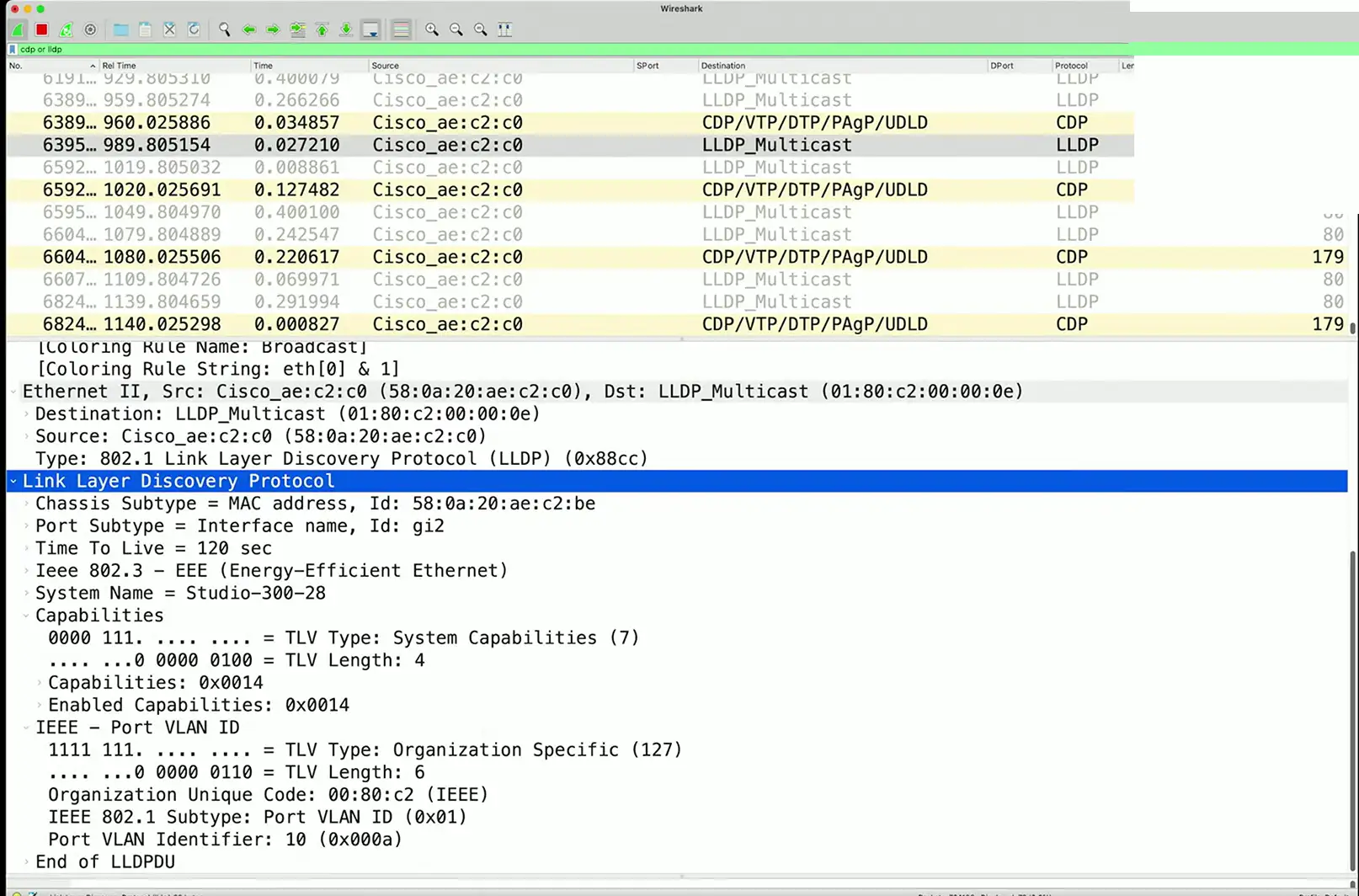
Discovering network devices
Switched networks can be a challenge
- Many interfaces
- Each interface can have a very different configuration
- Identify the port number, MAC address, VLAN ID, etc.
CDP — Cisco Discovery Protocol
LLDP — Link Layer Discovery Protocol
Speed test sites
Bandwidth testing
- Transfer a file, measure the throughput
Provide useful pre- and post-change analysis
- Test, install firewall/packet shaper, test again
Measure at different times of the day
- Can be automated or manual
Not all sites are the same
- Number of servers (point of presence — POP)
- Bandwidth at the POP
- Testing methodology
ISP sites
- speedtest.xfinity.net
- www.att.com/speedtest
fast.com
Speedof.me
speedtest.net
testmy.net
Command Line Tools
ping
Test reachability
- Determines round-trip time
- Uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
One of your primary troubleshooting tools
- Can you ping the host?
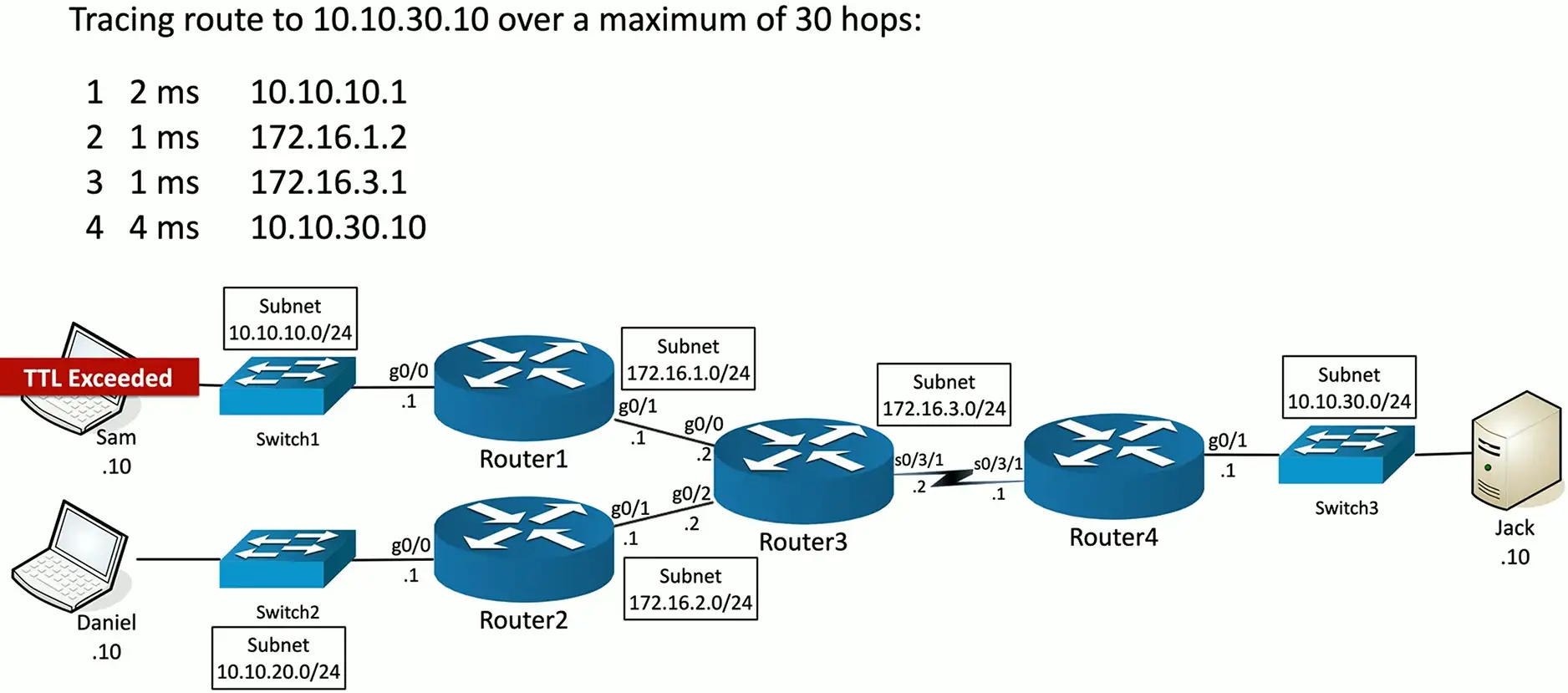
traceroute
Determine the route a packet takes to a destination
- Map the entire path
tracert(Windows) ortraceroute(Unix/Linux/macOS)
Take advantage of ICMP Time to Live Exceeded error message
- The time in TTL refers to hops, not seconds or minutes
- TTL = 1 is the first router, TTL = 2 is the second router, etc.
Not all devices will reply with ICMP Time Exceeded messages
- Some firewalls filter ICMP
- ICMP is low-priority for many devices
Flavors of traceroute
Not all traceroutes are the same
- Minor differences in the transmitted payload
Windows commonly sends ICMP echo requests
- Receives ICMP time exceeded messages
- And an ICMP echo reply from the final/destination device
- Unfortunately, outgoing ICMP is commonly filtered
Some operating systems allow you to specify the protocol used
- Linux, Unix, macOS, etc.
The mechanics of traceroute
Info
Now, almost every major DNS provider/Website is filtering ICMP exceed errors.
nslookup And dig
Lookup information from DNS servers
- Canonical names, IP addresses, cache timers, etc.
nslookup
- Both Windows and POSIX-based
- Lookup names and IP addresses
- Deprecated (use dig instead)
dig (Domain Information Groper)
- More advanced domain information
- Probably your first choice
- Windows: https://www.isc.org/downloads/bind/
tcpdump
Capture packets from the command line
- Very convenient
Available in most Unix/Linux OSes
- Included with macOS, available for Windows (WinDump)
Apply filters, view in real-time
- Quickly identify traffic patterns
Save the data, use in another application
- Written in standard pcap format
Can be an overwhelming amount of data
- Takes a bit of practice to parse and filter
netstat
Network statistics
- Many OSes
netstat -a
- Show all active connections
netstat -b
- Show binaries (Windows)
netstat -n
- Do not resolve name (show only IPs)
ipconfig/ifconfig/ip
Most of your troubleshooting starts with your IP address
- Ping your local router/gateway
Determine TCP/IP and network adapter information
- And some additional IP details
ipconfig — Windows TCP/IP configuration
ifconfig — Linux interface configuration
ip addresss — The latest Linux utility
Address Resolution Protocol
Determine a MAC address based on an IP address
- You need the hardware address to communicate
arp -a
- View local ARP table
Hardware Tools
Tone generator
Where does that wire go?
- Follow the tone
Tone generator
- Puts an analog sound on the wire
Inductive probe
- Doesn’t need to touch the copper
- Hear through a small speaker
Using the tone generator and probe
Easy wire tracing
- Even in complex environments
Connect the tone generator to the wire
- Modular jack
- Coax
- Punch down connectors
Use the probe to locate the sound
- The two-tone sound is easy to find
Cable testers
Relatively simple
- Continuity test
- A simple wire map
Can identify missing pins
- Or crossed wires
Not usually used for frequency testing
- Crosstalk, signal loss, etc.
Taps and port mirrors
Intercept network traffic
- Send a copy to a packet capture device
Physical taps
- Disconnect the link, put a tap in the middle
- Can be an active or passive tap
Port mirror
- Port redirection, SPAN (Switched Port Analyzer)
- Software based tap
- Limited functionality, but can work well in a pinch
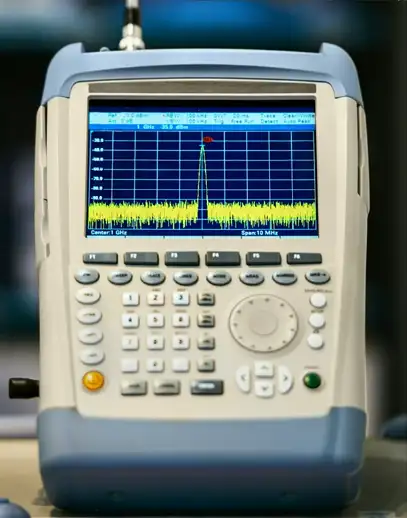
Wireless Survey Tools
- Signal coverage
- Potential interference
- Built-in tools
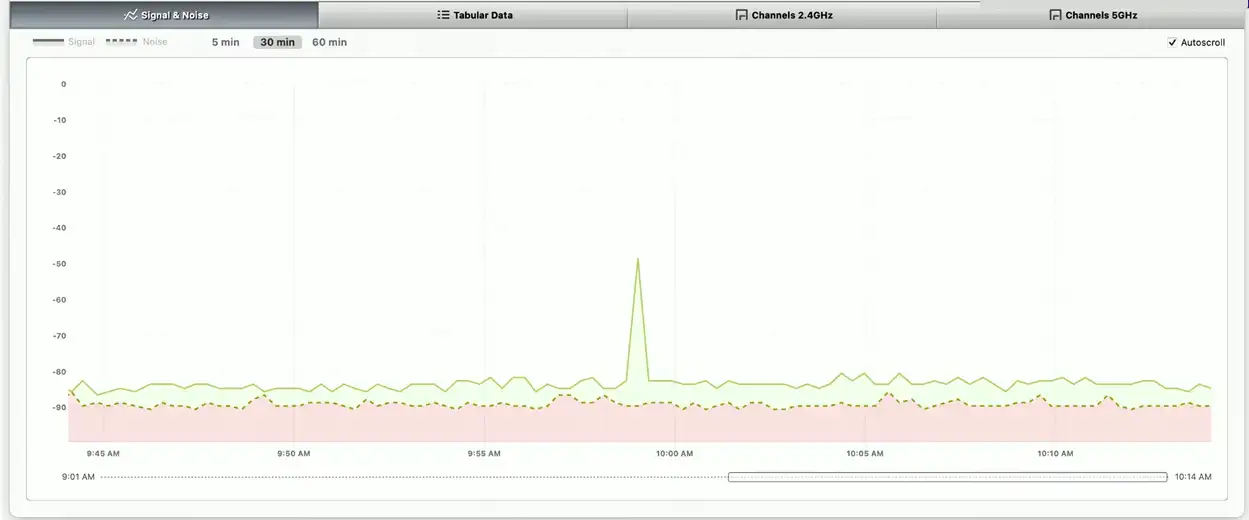
Wi-Fi Analyzer
Hardware-based Wi-Fi analysis
- Avoids OS limitations
- View all the 802.11 information in the air
View Wi-Fi information
- Frequencies/channels, signal strength, access points, interference, wireless devices
Get frequency information from a spectrum analyzer
- Useful when many devices are part of the bigger picture
Visual fault locator
A flashlight for optical fiber
- Shine a bright light down the fiber
Light will show through the fiber jacket where fiber is broken
- You may need to turn the lights out
Relatively low-tech
- But very efficient
Basic Network Device Commands
Basic Platform Commands
There are some commands that are common across switch and router manufacturers
- It’s remarkable how similar they can be
- Once you know one, you effectively know them all
Not all devices use exactly the same syntax
- Refer to the documentation for specifics
- The fundamentals are the same, however
Learn the technology
- The commands will come naturally
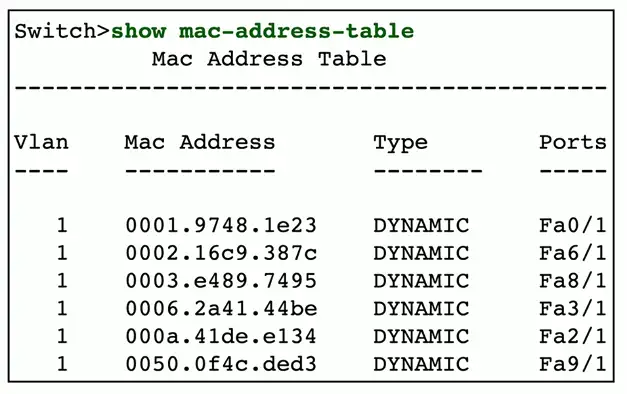
show mac-address-table
All switches maintain a MAC address table
- Media Access Control addresses
- The Ethernet hardware
View the MAC address table
- The
showcommand - Many options are available for showing information
Switch forwarding uses this table
- This MAC address is connected to this interface
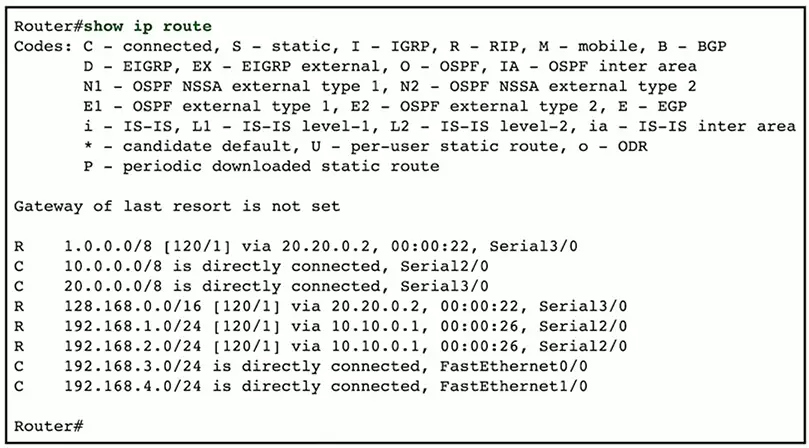
show route
Routers maintain a list of next hops
- The routing table
View the current routing table
- Dynamic routes can change
- Static routes must be manually configured
Use this list to find errors in the routes
- Or use the table to manually determine the next hop
- Useful when troubleshooting
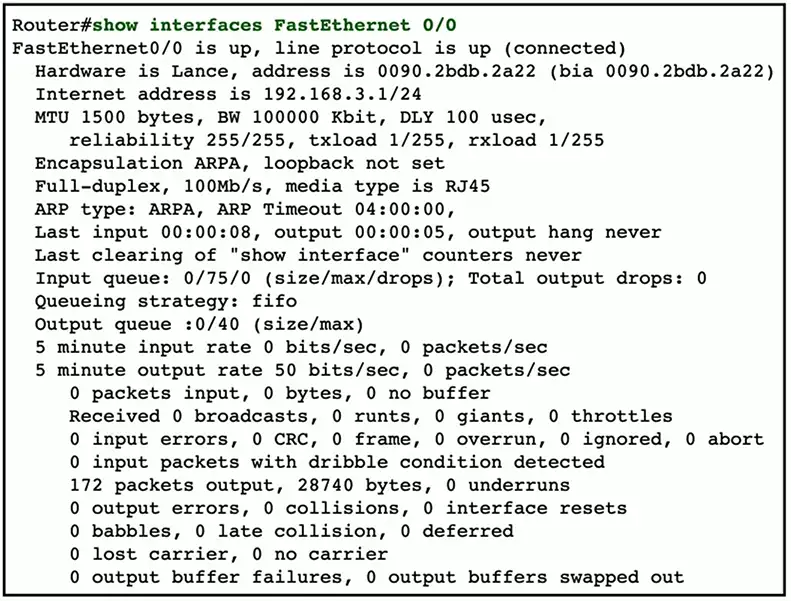
show interface
The status of an interface
- Up, down, connected, disabled, speed, duplex, etc.
View configuration information
- Speed, MTU, encapsulation, etc.
Identify errors
- Problems with the interface
- CRC errors, drops, input, and output errors
View overall performance
- Total frames, broadcasts
- Queue capacity
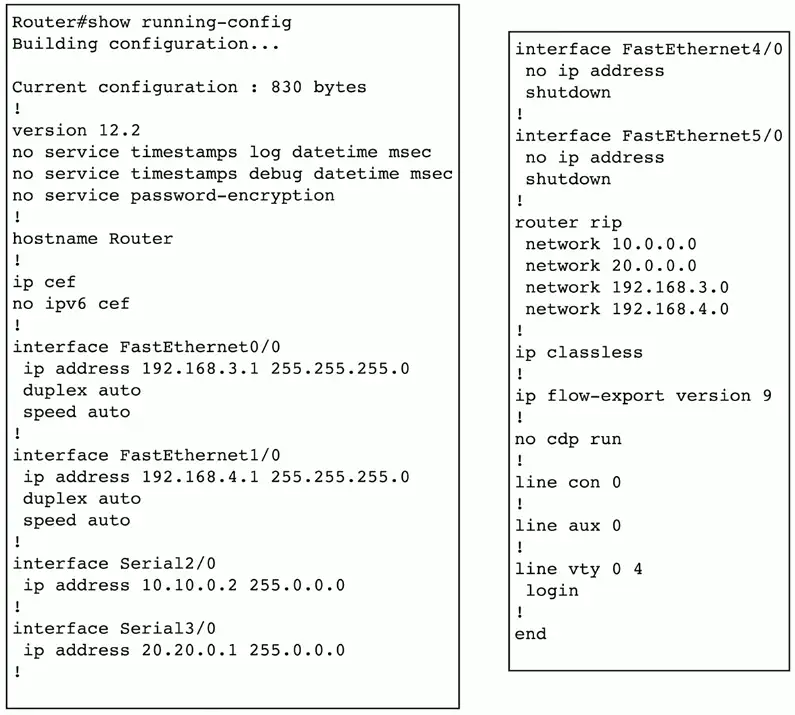
show config
Every device has a configuration
- View the device settings
Display the currently running configuration
- Or configuration settings stored on the device
- Everything in one place
Requires a bit of training
- Learn the syntax
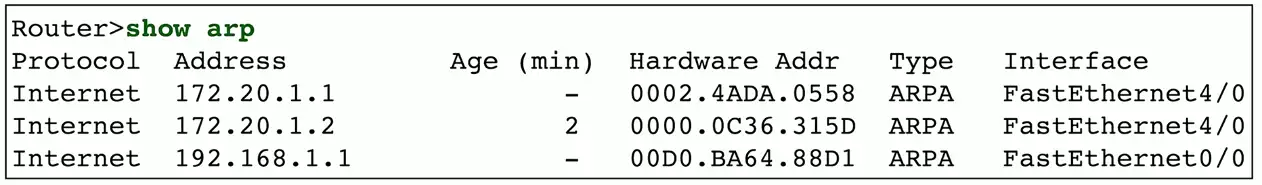
show arp
View ARP protocol information
- Address Resolution Protocol
Useful when troubleshooting connectivity
- Do we see the MAC address associated with an IP address?
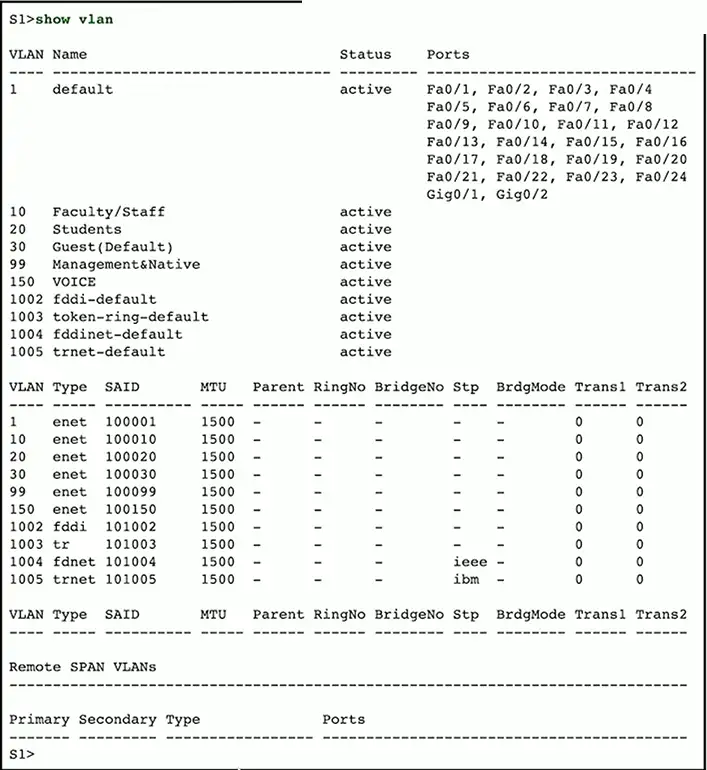
show vlan
View the VLANs associated with switch interfaces
- Virtual Local Area Network ID
View default VLAN ID and assigned VLAN ID numbers
- Confirm the assignment for each interface
show power
Display power-related information
- Power supply status, Power over Ethernet usage
Monitor power usage
- Available, used, and remaining power
Manage PoE devices
- Plan for future PoE devices and troubleshooting power issues