Network Security Features
Device Security
Disable unnecessary ports and services
Every open port is a possible entry point
- Close everything except required ports
Control access with a firewall
- NGFW would be ideal
Unused or unknown services
- Installed with the OS or from other applications
Applications with broad port ranges
- Open port 0 through 65,535
Use Nmap or similar port scanner to verify
- Ongoing monitoring is important
Changing default credentials
Most devices have default usernames and passwords
- Change yours.
The right credentials provide full control
- Administrator access
Very easy to find the defaults for your access point or router
Port security
Prevent unauthorized users from connecting to a switch interface
- Alert or disable the port
Based on the source MAC address
- Even if the forwarded from elsewhere
Each port has its own config
- Unique rules for every interface
Port security operation
Configure a maximum number of source MAC addresses on an interface
- You decide how many is too many
- You can also configure specific MAC addresses
The switch monitors the number of unique MAC addresses
- Maintains a list of every device source MAC address
Once you exceed the maximum, port security activates
- Default is to disable the interface
Disable unused interface
Enabled physical ports
- Conference rooms
- Break rooms
Administratively disable unused ports
- More to maintain, but more secure
Network Access Control (NAC)
- 802.1X controls
- You can’t communicate unless you are authenticated
MAC filtering
Media Access Control
- The “hardware” address
Limit access through the physical hardware address
- Keeps the neighbors out
- Additional administration with visitors
Easy to find working MAC addresses through wireless LAN analysis
- MAC addresses can be spoofed
- Free open-source software
Security through security
- If you know the method, you can easily defeat it
Key management system
Services are everywhere
- On-premises, cloud-based
- Many keys for many services
Manage all keys from a centralized manager
- Often provided as third-party software
- Separate the encryption keys from the data
All key management from one console
- Create keys for a specific service or cloud (SSL/TLS, SSH, etc.)
- Associate keys with specific users
- Rotate keys on regular intervals
- Log key use and important events
Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Allow or disallow traffic
- Groupings of categories
- Source IP, Designation IP, port number, time of day, application, etc.
Restrict access to network devices
- Limit by IP address or other identifier
- Prevent regular user/non-admin access
Can be implemented in many ways
- Router, firewall, OS policies, etc.
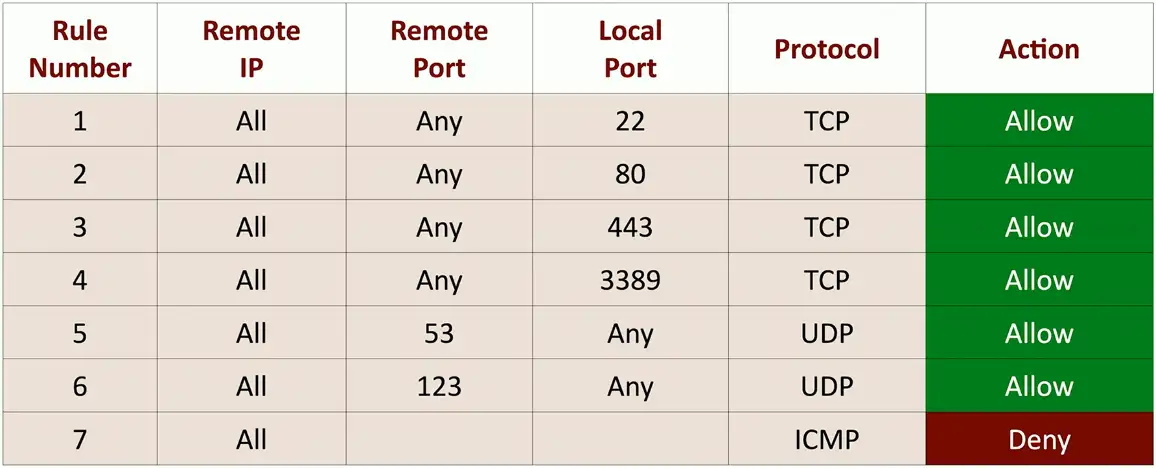
Firewall Rules
A logical path
- Usually top-to-bottom
Can be very general or very specific
- Specific rules are usually at the top
Implicit deny
- Most firewalls include deny at the bottom
- Even if you didn’t put one
URL filtering
Allow or restrict based on Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
- Also called a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI)
- Allow list/Block list
Managed by category
- Auction, Hacking, Malware, Travel, Recreation, etc.
Can have limited control
- URLs aren’t the only way to surf
Often integrated into an NGFW
- Filters traffic based on category or specific URL
Content Filtering
Control traffic based on data within the content
- URL filtering, website category filtering
Corporate control of outbound and inbound data
- Sensitive materials
Control of inappropriate content
- Not safe for work
- Parental controls
Protection against evil
- Anti-virus, anti-malware
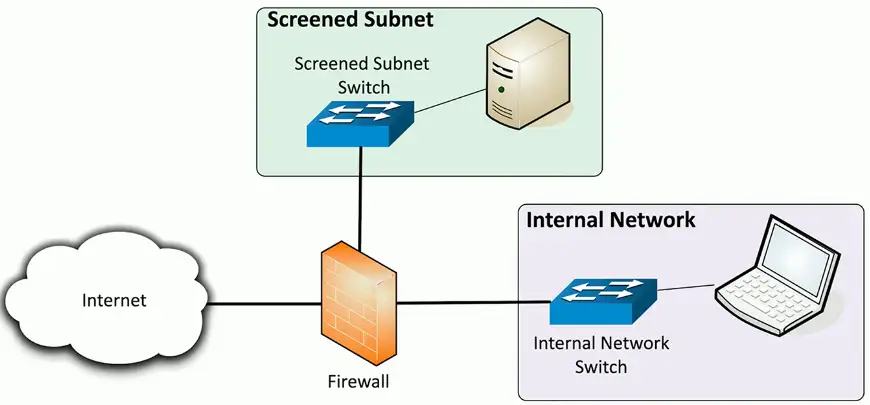
Screened subnet
An additional layer of security between you and the Internet
- Public access to public resources
- Private data remains inaccessible
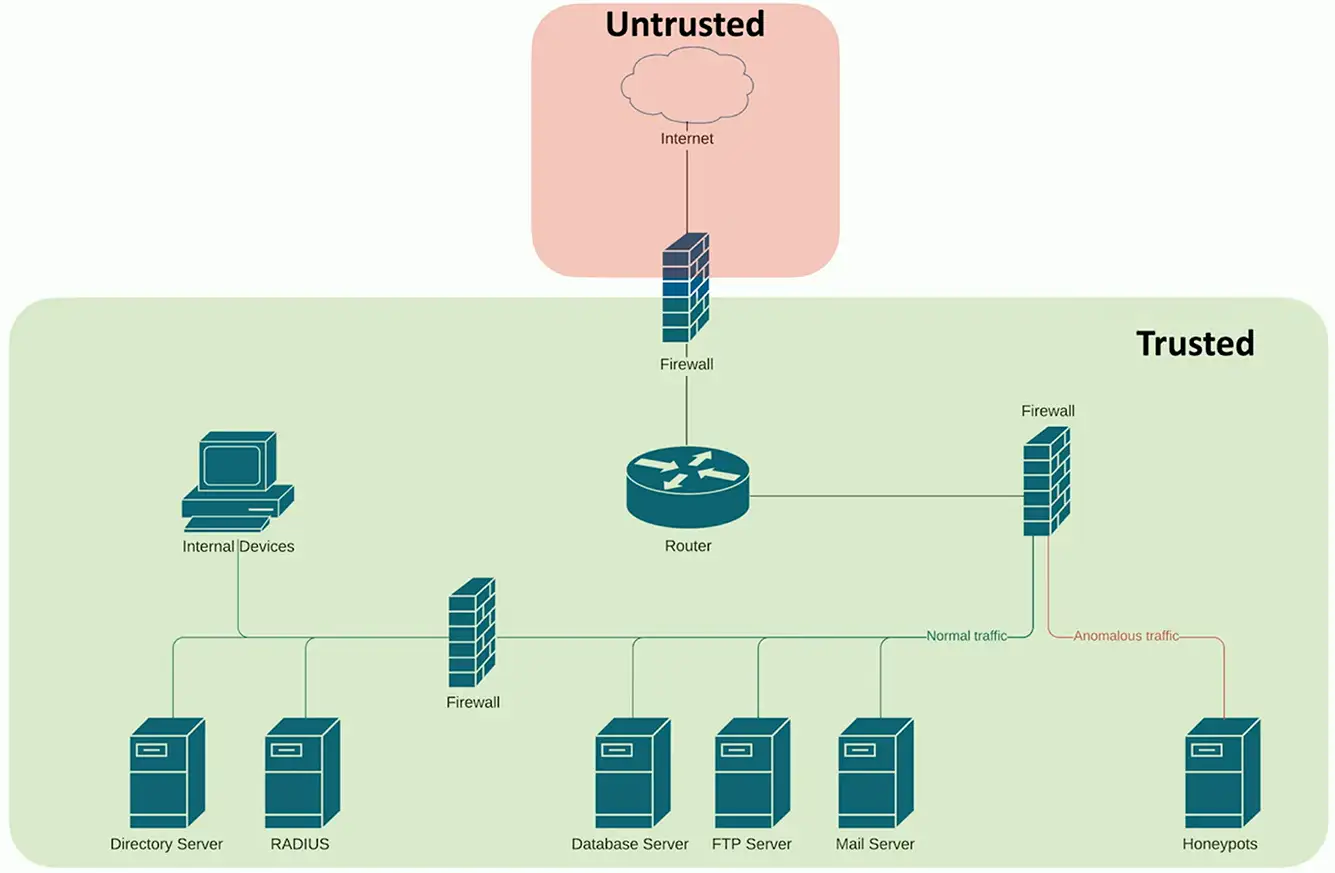
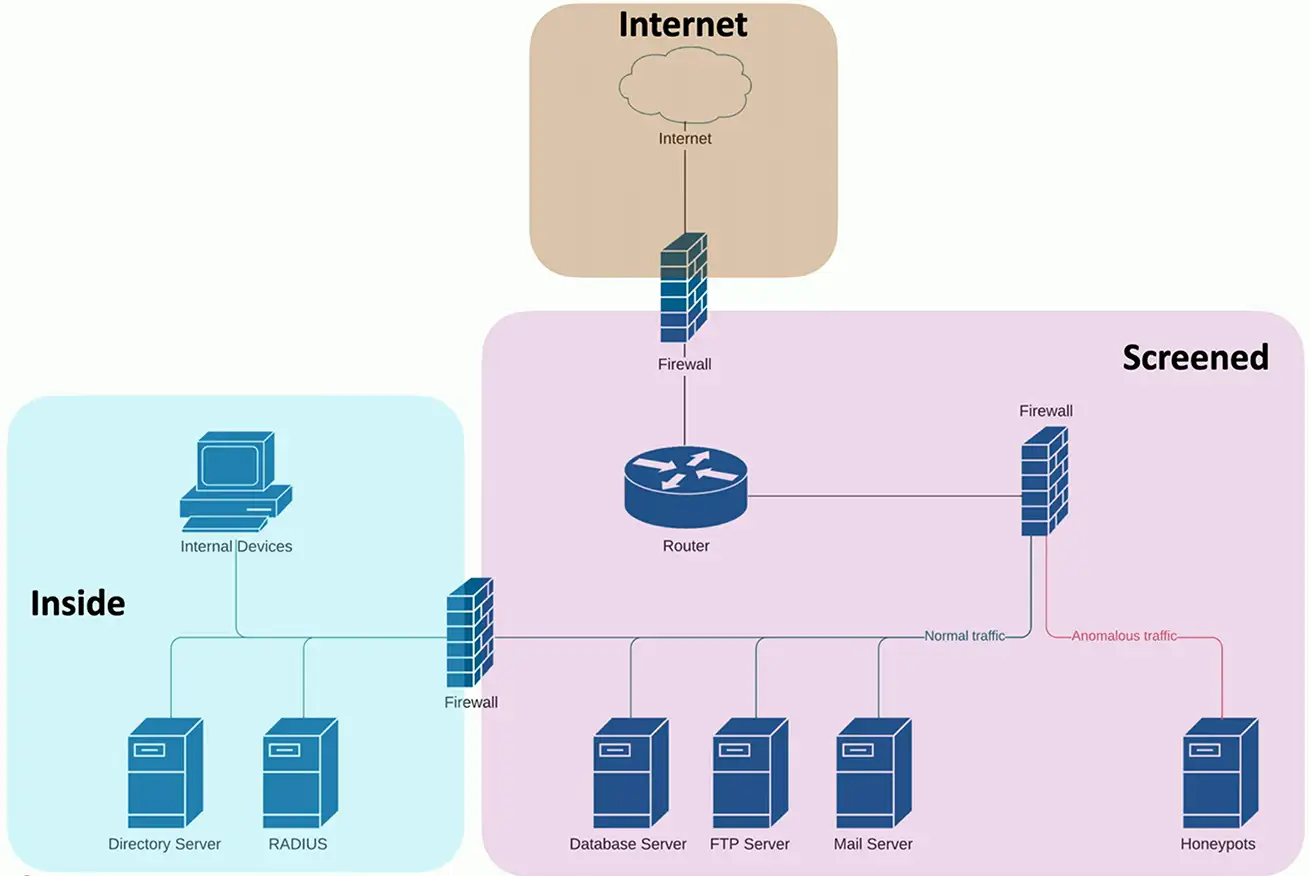
Security Zones
Zone-based security technologies
- More flexible (and secure) than IP address ranges
Each area of the network is associated with a zone
- Trusted, untrusted
- Internal, external
- Inside, Internet, Servers, Databases, Screened
This simplifies security policies
- Trusted to Untrusted
- Untrusted to Screened
- Untrusted to Trusted