Network Security Concepts
Security Concepts
Data in transit
Data transmitted over the network
- Also called data in motion
Not much protection as it travels
- Many switches, routers, devices
Network-based protection
- Firewall, IPS
Provide transport encryption
- TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- IPsec (Internet Protocol Security)
Data at rest
The data is on a storage device
- Hard drive, SSD, flash drive, etc.
Encrypt the data
- Whole disk encryption
- Database encryption
- File or folder-level encryption
Apply permissions
- Access control lists
- Only authorized users can access the data
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Policies, procedures, hardware, software, people
- Digital certificates: create, distribute, manage, store, revoke
This is a big, big, endeavor
- Lots of planning
Also refers to the binding of public keys to people or devices
- The certificate authority
- It’s all about trust
Digital Certificates
A public key certificate
- Binds a public key with a digital signature
- And other details about the keyholder
A digital signature adds trust
- PKI uses Certificate Authorities for additional trust
- Web of Trust adds other users for additional trust
Certificate creation can be built into the OS
- Part of Windows Domain services
- Many 3rd-party options
Certificate Authorities
You connect to a random website
- Do you trust it?
Need a good way to trust an unknown entity
- Use a trusted third-party
- An authority
Certificate Authority (CA) has digitally signed the website certificate
- You trust the CA, therefore you trust the website
- Real-time verification
Self-signed Certificates
Internal certificates don’t need to be signed by a public CA
- Your company is the only one going to use it
- No need to purchase trust for devices that already trust you
Built your own CA
- Issue your own certificates signed by your own CA
Install the CA certificate/trusted chain on all devices
- They’ll now trust any certificates signed by your internal CA
- Works exactly like a certificate you purchased
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Applications are available anywhere
- Desktop, browser, mobile device, etc.
Data can be located anywhere
- Cloud storage, private data centers, etc.
Many applications users
- Employees, vendors, contractors, customers
Give the right permissions to the right people at the right time
- Prevent unauthorized access
Identity lifecycle management
- Every entity (human and non-human) gets a digital identity
Access control
- An entity only gets access to what they need
Authentication and authorization
- Entities must prove they are who they claim to be
identity governance
- Track an entity’s resource access
- May be a regulatory requirement
Least Privilege
Rights and permissions should be set to the bare minimum
- You only get exactly what’s needed to complete your objective
All user accounts must be limited
- Applications should run with minimal privileges
Don’t allow users to run with administrative privileges
- Limits the scope of malicious behavior
Role-based Access Control (RBAC)
You have a role in your organization
- Manager, director, team lead, project manager
Administrators provide access based on the role of the user
- Rights are gained implicitly instead of explicitly
On Windows, use Groups to provide role-based access control
- You are in shipping and receiving, so you can use the shipping software
- You are the manager, so you can review shipping logs
Geographic Restrictions
Network location
- Identify based on IP subnet
- Can be difficult with mobile devices
Geolocation — determine a user’s location
- GPS — mobile devices, very accurate
- 802.11 wireless, less accurate
- IP address, not very accurate
Geo-fencing
- Automatically allow or restrict access when the user is in a particular location
- Don’t allow this app to run unless you’re near the office
Cameras
CCTV (Closed circuit television)
- Can replace physical guards
Camera features are important
- Motion recognition can alarm and alert when something moves
- Object detection can identify a license plate, a person’s face, or a type of animal
Often many cameras
- Networked together and recorded over time
Door Locks
Conventional
- Lock and key
Deadbolt
- Physical bolt
Electronic
- Keyless, PIN
Token-based
- RFID badge, magnetic swipe card, or key fob
Biometric
- Hand, fingers, or retina
Multifactor
- Smart card and PIN
Authentication
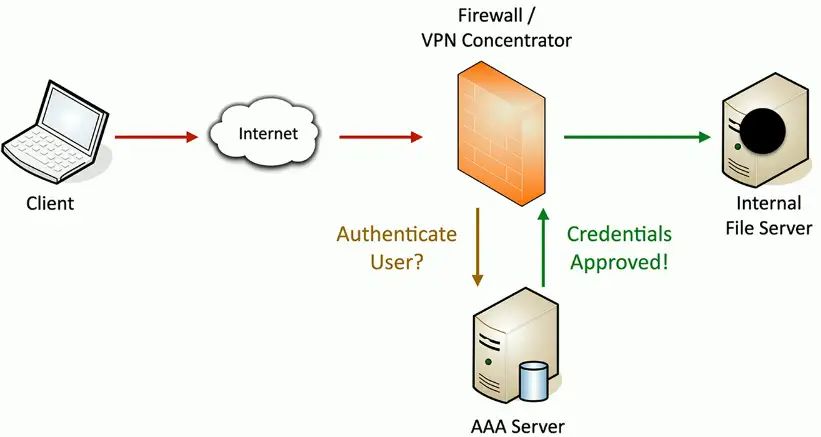
AAA framework
Identification
- This is who you claim to be
- Usually your username
Authentication
- Prove you are who you say you are
- Password and other authentication factors
Authorization
- Based on your identification and authentication, what access do you have?
Accounting
- Resources used: Login time, data sent and received, logout time
Gaining Access
Single sign-on (SSO)
Provide credentials one time
- Get access to all available or assigned resources
- No additional authentication required
Usually limited by time
- A single authentication can work for 24 hours
- Authenticate again after the time expires
The underlying authentication infrastructure must support SSO
- No always an option
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service)
One of the more common AAA protocols
- Supported on a wide variety of platforms and devices
- Not just for dial-in
Centralize authentication for users
- Routers, switches, firewalls
- Server authentication
- Remote VPN access
- 802.X network access
RADIUS services available on almost any server OS
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
Protocol for reading and writing directories over an IP network
- An organized set of records, like a phone directory
X.500 specification was written by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU)
- They know directories!
DAP ran on the OSI protocol stack
- LDAP is lightweight
LDAP is the protocol used to query and update an X.500 directory
- Used in Windows Active Directory, Apple OpenDirectory, Novell eDirectory, etc.
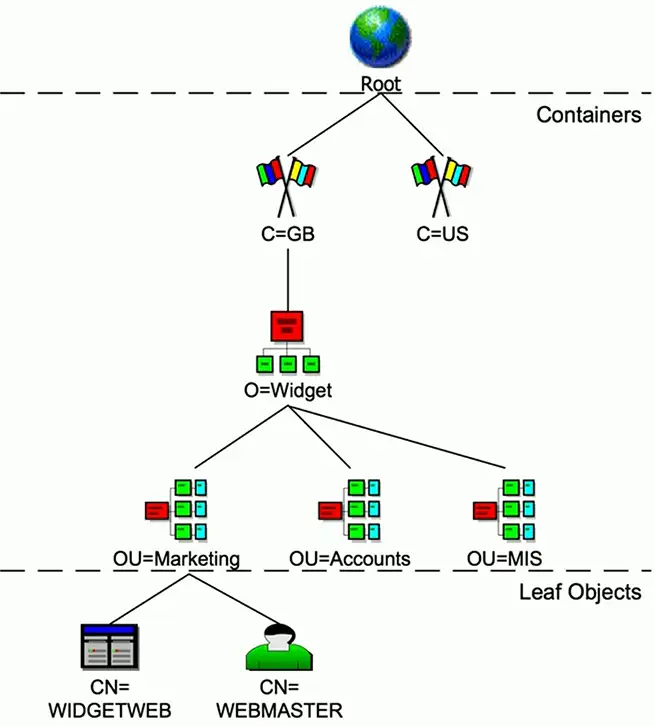
X.500 Distinguished Names
attribute=value pairs
Most specific attribute is listed first
- This may be similar to the way you already think
| Attribute | Field | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| CN | Common Name | Identifies the person or object |
| OU | Organizational Unit | A unit or department within the organization |
| O | Organization | The name of the organization |
| L | Locality | Usually a city or area |
| ST | State | A state, province, or country within a country |
| C | Country | The country’s 2-character ISO code (such as c=US or c=GB) |
| DC | Domain Component | Components of the object’s domain |
X.500 Directory Information Tree
Hierarchical structure
- Builds a tree
Container objects
- Country, organization, organizational units
Leaf objects
- Users, computers, printers, files
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)
Open standard for authentication and authorization
- You can authenticate through a third party to gain access
- One standard does it all, sort of
Not originally designed for mobile apps
- This has been SAML’s largest roadblock
The SAML authentication flow
TACACS
Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System
- Remote authentication protocol
- Created to control access to dial-up lines to ARPANET
TACACS+
- The latest version of TACACS, not backwards compatible
- More authentication requests and response codes
- Released as an open standard in 1993
Multifactor Authentication
Prove who you are
- Use different methods
- A memorized password
- A mobile app
- Your GPS location
Factors
- Something you know
- Something you have
- Something you are
- Somewhere you are
TOTP
Time-based One-Time Password algorithm
- Use a secret key and the time of day
- No incremental counter
Secret key is configured ahead of time
- Timestamps are synchronized via NTP
Timestamp usually increments every 30 seconds
- Put in your username, password, and TOTP code
One of the more common OTP methods
- Used by Google, Facebook, Microsoft, etc.
Security Technologies
Honeypots
Attract the bad guys
- And trap them there
The “attacker” is probably a machine
- Makes for interesting recon
Honeypots
- Create a virtual world to explore
Many options
- Most are open source and available to download
Constant battle to discern the real from the fake
Honeynets
A real network includes more than single device
- Servers, workstations, routers, switches, firewalls
Honeynets
- Build a larger deception network with one or more honeypots
More than one source of information
- Stop spammers — https://projecthoneypot.org
Risk
An exposure to harm or danger
- The possibility of something bad happening
An important consideration
- Growth brings risk
- It’s useful to get ahead of any potential problems
Most things have an associated risk
- Manage potential risk
- Qualify internal and external threats
- Risk analysis helps plan for contingencies
Vulnerabilities
A weakness in a system
- Allows the bad guys to gain access or cause a security breach
Some vulnerabilities are never discovered
- Or discovered after years of use
Many vulnerability types
- Data injection
- Broken authentication process
- Sensitive data exposure
- Security misconfiguration
Exploits
Take advantage of a vulnerability
- Gain control of a system
- Modify data
- Disable a service
Many exploit methods
- Built to take advantage of a vulnerability
- May be complex
Threat
A vulnerability can be exploited by a threat
- May be intentional (attacker) or accidental (fire, flood, etc.)
- Many of these threats are external to the organization
A resource can have a vulnerability
- The vulnerability can be exploited by a threat agent
- The threat agent takes a threat action to exploit the vulnerability
The result is a loss of security
- Data breach, system failure, data theft
The CIA Triad
Combination of principles
- The fundamentals of security
- Sometimes references as the AIC triad
Confidentiality
- Prevent disclosure of information to unauthorized individuals or systems
Integrity
- Messages can’t be modified without detection
Availability
- Systems and networks must be up and running
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance
- Meeting the standards of laws, policies, and regulations
A healthy catalog of regulations and laws
- Across many aspects of business and life
- Many are industry-specific or situational
Penalties
- Fines, incarceration, loss of employment
Scope
- Covers national, territory, or state laws
- Domestic and international requirements
Data Localization
Data from a region or country is stored within the borders of that region or country
- Data collected in Vegas stays in Vegas
Laws may prohibit where data is stored
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- A complex mesh of technology and legalities
Where is your data stored?
- Compliance laws may prohibit moving data out of the country
GDPR — General Data Protection Regulation
European Union Regulation
- Data protection and privacy for individuals in the EU
- Name, address, photo, email address, bank details, posts on social media, medical information, a computer’s IP address, etc.
Controls personal data
- Data collected on EU citizens must be stored in the EU
- Users can decide where their data goes
- Can request removal of data from search engines
Gives “data subjects” control of their personal data
- A right to be forgotten
PCI DSS
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
- A standard for protecting credit cards
Six control objectives
- Build and maintain a secure network and systems
- Protect cardholder data
- Maintain a vulnerability management program
- Implement strong access control measures
- Regularly monitor and test networks
- Maintain an information security policy
Segmentation Enforcement
Segmenting the network
Physical, logical or virtual segmentation
- Devices, VLANs, virtual networks
Performance
- High-bandwidth applications
Security
- Users should not talk directly to database servers
- The only applications in the core are SQL and SSH
Compliance
- Mandated segmentation (PCI compliance)
- Makes change control much easier
IoT (Internet of Things)
Sensors
- Heating and cooling, lighting
Smart devices
- Home automation, video doorbells
Wearable technology
- Watches, health monitors
Weak defaults
- IoT manufacturers are not security professionals
IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things)
IoT for companies
- Machine to machine communication
Segmentation is just as important
- More data is at stake
Facility automation
- Temperature, air quality, lighting
Industrial equipment/ICS monitoring
- Oil and gas, robotics, medical devices
- Specialized monitoring systems
- Wired and wireless connectivity
SCADA/ICS
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System
- Large-scale, multisite Industrial Control Systems (ICS)
PC manages equipment
- Power generation, refining, manufacturing equipment
- Facilities, industrial, energy, logistics
Distributed control systems
- Real-time information
- System control
Requires extensive segmentation
- No access from the outside
Operational Technology (OT)
The hardware and software for industrial equipment
- Electric grids, traffic control, manufacturing plants, etc.
This is more than a web server failing
- Power grid drops offline
- All traffic lights are green
- Manufacturing plant shuts down
Requires a different approach
- A much more critical security posture
Guest Networks
A network for visitors
- No access to the private network
Separate wireless network
- For guests only
Controlled access
- Password or captive portal
Fire walled from the rest of the network
- Internet Access only
BYOD
Bring Your Own Device
- Bring Your Own Technology
Employee owns the device
- Need to meet the company’s requirements
A challenge to secure
- Segment the device from the internal network
- It’s both a home device and a work device